Contents

Cell and its Structure
Description: A cell is the basic unit of life, containing organelles like nucleus and mitochondria, enclosed by a cell membrane.

Micro-organisms
Description: Microorganisms are tiny living organisms invisible to the naked eye, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protists.

Respiration in Plants
Description: Respiration in plants involves the process of converting glucose into energy, releasing carbon dioxide and water as byproducts.

Respiration in Animals
Description: Respiration in animals involves inhaling oxygen and exhaling carbon dioxide to produce energy through cellular respiration in various body tissues.

Reproduction in Plants
Description: Reproduction in plants involves the creation of new plants through processes like pollination, fertilization, and seed dispersal.
Reproduction in Animals
Description: Reproduction in animals involves the creation of offspring through sexual or asexual means, ensuring the continuation of the species.

Conservation of Natural Resources
Description: Conservation of natural resources involves sustainable management to ensure their availability for present and future generations, preserving biodiversity and ecosystems.

Elements
Description: Elements are fundamental substances made up of atoms with the same number of protons, defining their unique chemical properties.

Atoms & Molecules
Description: Atoms are basic units of matter, consisting of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Molecules are groups of atoms bonded together chemically.

States of Matter
Description: States of matter are solid, liquid, gas, and plasma, determined by particle arrangement, energy, and interaction at given conditions.

Metal and Non-Metal
Description: Metals are elements with metallic properties, conducting heat and electricity. Non-metals lack these properties and are often insulators.

Physical & Chemical Change
Description: Physical change alters the form of a substance without changing its chemical composition, while chemical change involves chemical reactions.
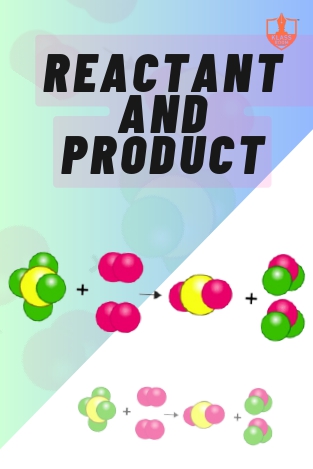
Reactant & Product
Description: Reactants are substances entering a chemical reaction, while products are substances formed as a result of that reaction.

Motion & Time
Description: Motion is the change in position of an object over time, while time is a measure of duration or intervals.

Force & Pressure
Description: Force is a push or pull applied to an object, while pressure is force distributed over a surface area, measured in Pascals.

Laws of Motion
Description: Newton's laws of motion describe how objects move: inertia, force equals mass times acceleration, and action and reaction forces.

Work & Energy
Description: Work is the transfer of energy by a force acting on an object, while energy is the capacity to do work.

Light
Description: Light is electromagnetic radiation visible to the human eye, carrying energy, illuminating objects, and enabling vision and photosynthesis.

Electric Current
Description: Electric current is the flow of electric charge, usually carried by electrons through a conductor, resulting from voltage difference.

Gravity
Description: Gravity is the natural force of attraction between objects with mass, causing them to move toward each other.