Contents
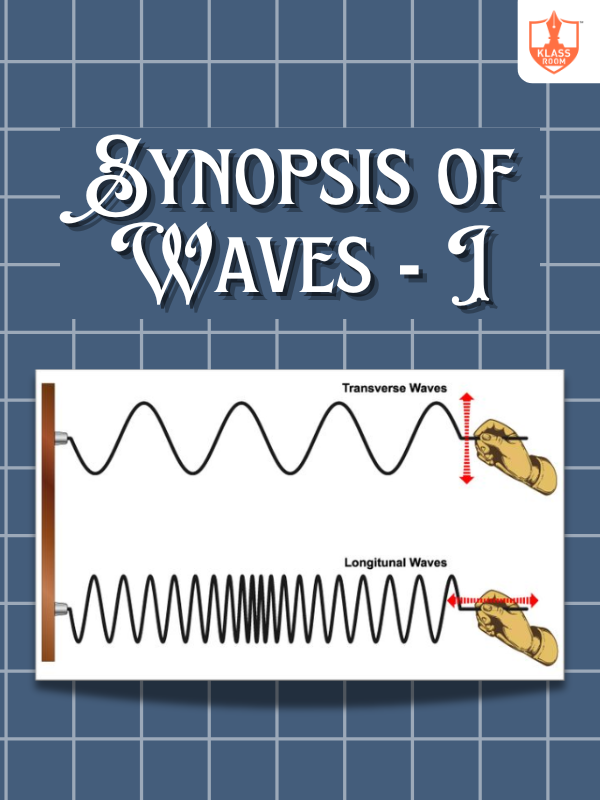
Synopsis of Waves - I
Description: Waves transfer energy without transporting matter, characterized by amplitude, frequency, wavelength, and velocity.

Synopsis of Waves - II
Description: Synopsis of Waves - II
Synopsis of Waves - III
Description: Wave equations describe displacement variations over time and space, governing wave motion principles.

Transverse and Longitudinal Waves - I
Description: Transverse waves oscillate perpendicular to propagation direction, like light and water waves.

Transverse and Longitudinal Waves - II
Description: Longitudinal waves oscillate parallel to propagation direction, seen in sound and seismic waves.

Transverse and Longitudinal Waves - III
Description: Compression and rarefaction regions define longitudinal waves, while crests and troughs define transverse waves.

Transverse and Longitudinal Waves - IV
Description: Both wave types obey reflection, refraction, superposition, and interference principles in different mediums.
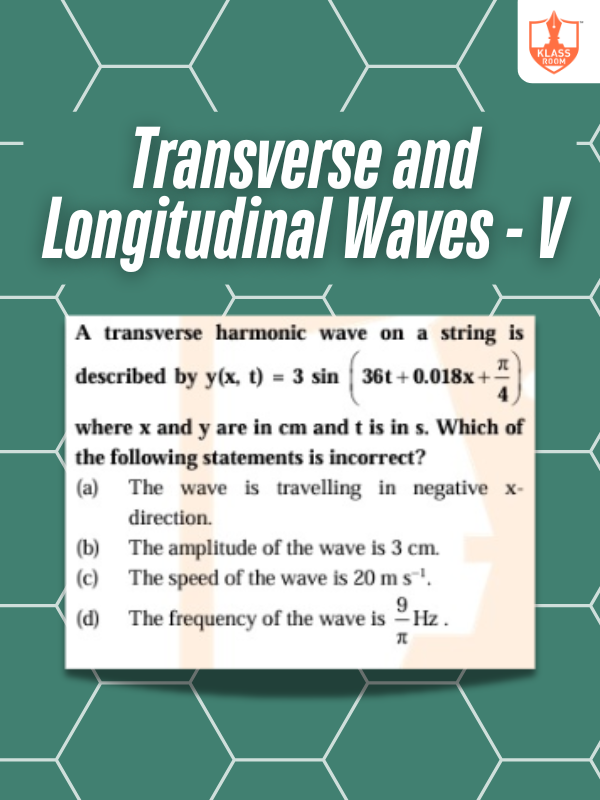
Transverse and Longitudinal Waves - V
Description: Transverse waves oscillate perpendicular to wave motion, like water ripples or light waves.

Transverse and Longitudinal Waves - VI
Description: Longitudinal waves oscillate parallel to wave motion, such as sound waves traveling through air.

Transverse and Longitudinal Waves - VII
Description: Crests and troughs characterize transverse waves, while compressions and rarefactions define longitudinal waves.

Superposition, Reflection of Waves, Beats & Doppler Effect - I
Description: Superposition principle states that overlapping waves combine algebraically, forming constructive or destructive interference patterns.

Superposition, Reflection of Waves, Beats & Doppler Effect - II
Description: Reflection of waves occurs when they bounce off a surface, obeying the law of reflection.

Superposition, Reflection of Waves, Beats & Doppler Effect - III
Description: Beats arise from interference between two close-frequency waves, producing alternating loud and soft sound patterns.

Superposition, Reflection of Waves, Beats & Doppler Effect - IV
Description: The Doppler effect describes frequency changes due to relative motion between source and observer.

Superposition, Reflection of Waves, Beats & Doppler Effect - V
Description: Moving toward a sound source increases perceived frequency; moving away decreases it, altering pitch.

Superposition, Reflection of Waves, Beats & Doppler Effect - VI
Description: Light also experiences the Doppler effect, with redshift for receding objects and blueshift for approaching ones.

Superposition, Reflection of Waves, Beats & Doppler Effect - VII
Description: Solves advanced problems on wave superposition, focusing on constructive and destructive interference patterns.

Superposition, Reflection of Waves, Beats & Doppler Effect - VIII
Description: Continues reflection of waves with boundary conditions and phase changes in different media.

Superposition, Reflection of Waves, Beats & Doppler Effect - IX
Description: Explores beat formation due to close frequency interference, emphasizing applications and graphical representation.

Superposition, Reflection of Waves, Beats & Doppler Effect - X
Description: Introduces Doppler effect for sound, analyzing apparent frequency shift due to relative motion of source.

Superposition, Reflection of Waves, Beats & Doppler Effect - XI
Description: Applies Doppler effect formulas in various cases including moving source, observer, and medium.

Superposition, Reflection of Waves, Beats & Doppler Effect - XII
Description: Solves complex, mixed problems combining all wave topics, reinforcing concepts through JEE-level applications and reasoning.


.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)
.png)

.png)
.png)
.png)