Contents
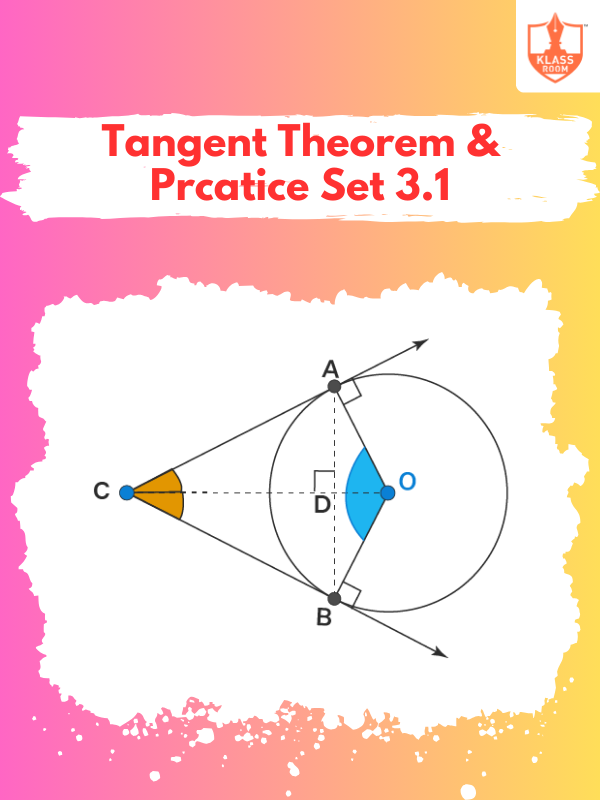
Tangent Theorem & Prcatice Set 3.1
Description: Tangent theorem states that a tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius at contact & Prcatice Set 3.1.

Problem Set Part - I & Practice 3.1 Part - II
Description: Solution of Problem Set Part - I & Practice 3.1 Part - II
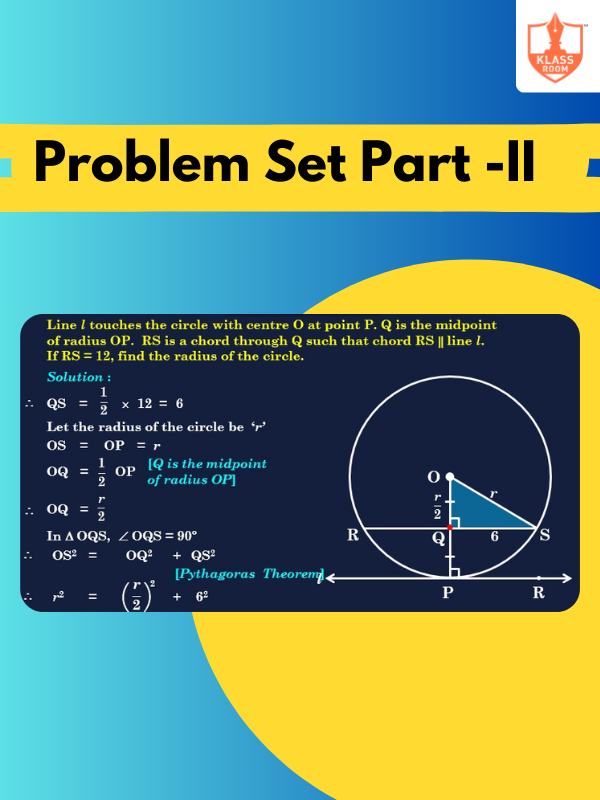
Problem Set Part -II
Description: Solution of Problem Set Part -II

Problem Set Part -III
Description: Solution of Problem Set Part -III
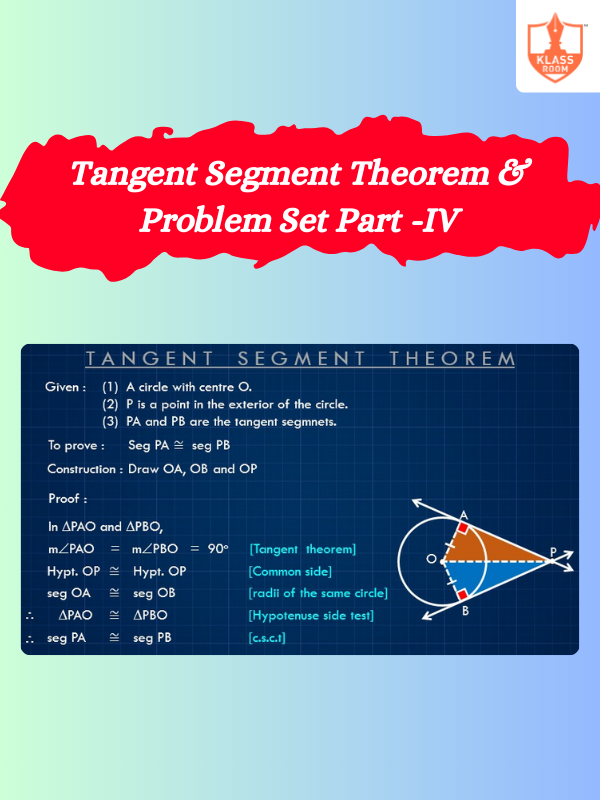
Tangent Segment Theorem & Problem Set Part -IV
Description: Tangent Segment Theorem states that two tangent segments from a point to a circle are equal in length & Problem Set Part -IV.

Practice Set 3.1 Part - III
Description: Solution of Prcatice Set 3.1 Part - III
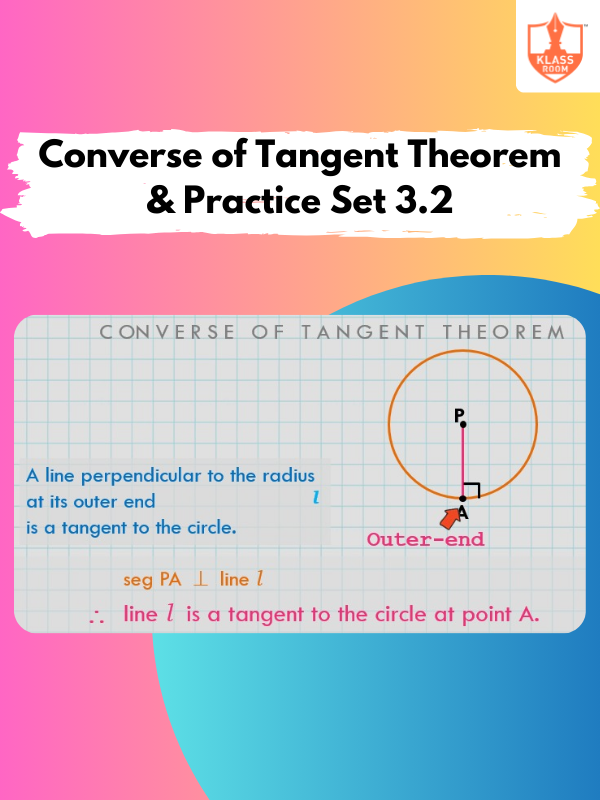
Converse of Tangent Theorem & Practice Set 3.2
Description: Converse of Tangent Theorem states that a line perpendicular to a radius is a tangent & Practice Set 3.2.
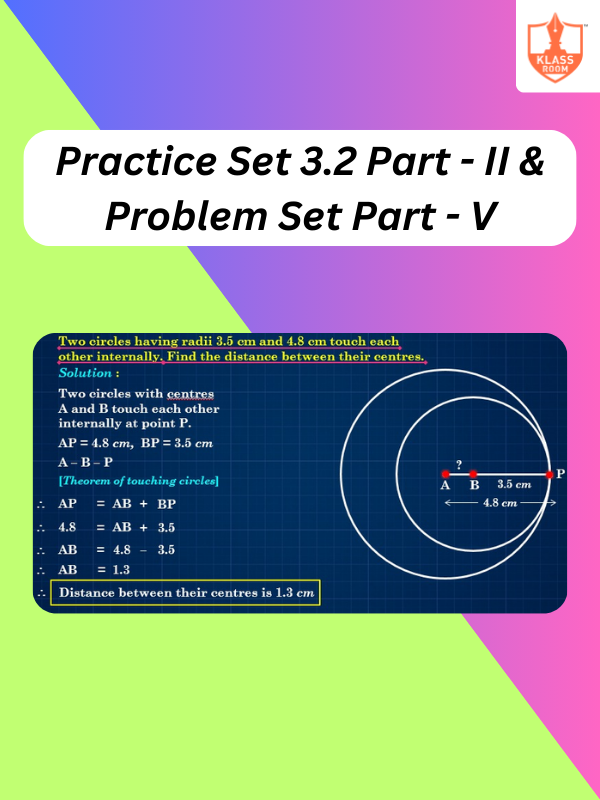
Practice Set 3.2 Part - II & Problem Set Part - V
Description: Solution of Practice Set 3.2 Part - II & Problem Set Part - V

Practice Set 3.2 Part - III
Description: Solution of Practice Set 3.2 Part - III

Problem Set Part - VI
Description: Solution of Problem Set Part - VI

Problem Set Part - VII & Practice Set 3.3
Description: Solution of Problem Set Part - VII & Practice Set 3.3
.png)
Corresponding Theorem (Arc & Chords)
Description: Corresponding Theorem states that equal chords in a circle subtend equal arcs and angles at the center.

Practice Set 3.3 Part - II & Practice Set 3.4
Description: Solution of Practice Set 3.3 Part - II & Practice Set 3.4

Problem Set Part - VII
Description: Solution of Problem Set Part - VII

Practice Set 3.4 Part - II & Problem Set Part - VII
Description: Solution of Practice Set 3.4 Part - II & Problem Set Part - VII

Practice Set 3.5 & Problem Set Part - VIII
Description: Solution of Practice Set 3.5 & Problem Set Part - VIII
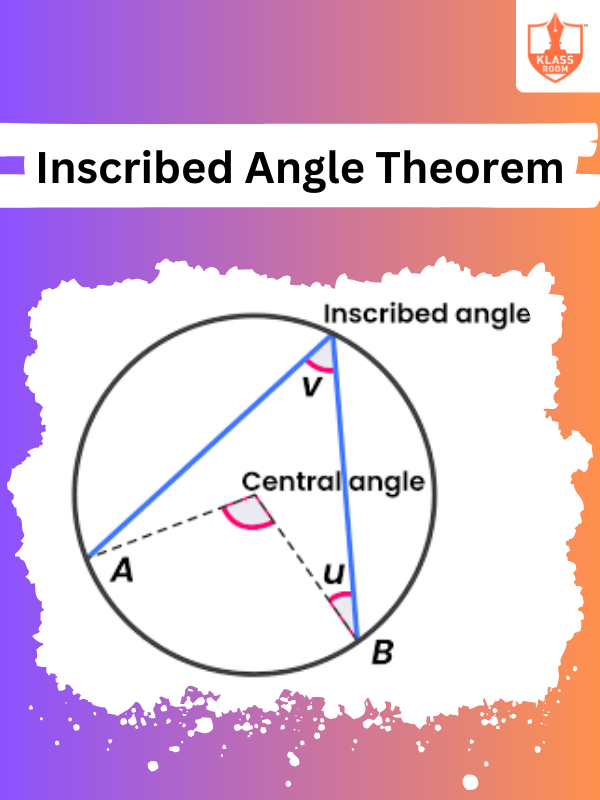
Inscribed Angle Theorem
Description: Inscribed Angle Theorem states that an angle inscribed in a circle is half the central angle subtended by the same arc.

Practice Set 3.4 Part-III
Description: Solution of Practice Set 3.4 Part-III
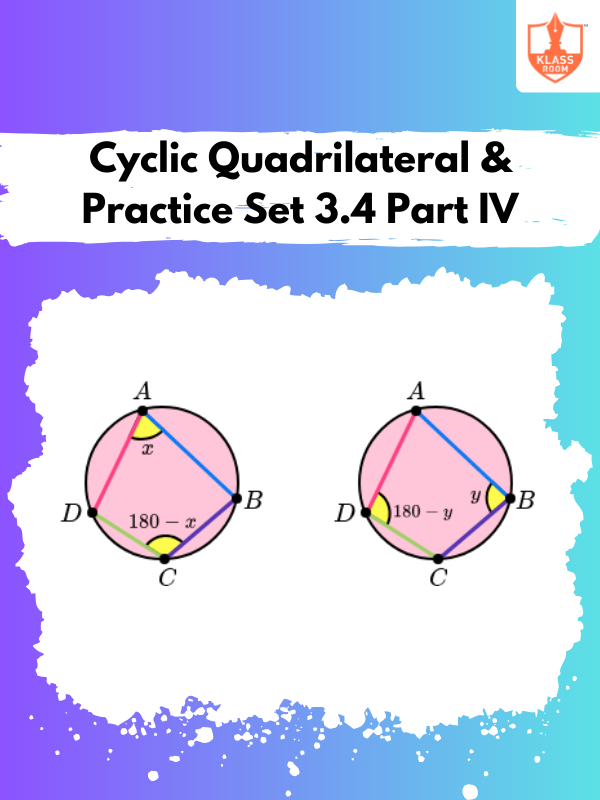
Cyclic Quadrilateral & Practice Set 3.4 Part IV
Description: A cyclic quadrilateral is a four-sided figure with all vertices lying on the circumference of a circle.
_Appllication-_I.png)
Corresponding Theorem (Arc & Chords) Application- I
Description: Theorem states that angles subtended by arcs at the center are double those subtended at circumference.
_Appllication-_II.png)
Corresponding Theorem (Arc & Chords) Application- II
Description: Equal chords in a circle subtend equal angles at the center and equal arcs on circumference.

Practice Set 3.4 Part V
Description: Solution of Practice Set 3.4 Part V
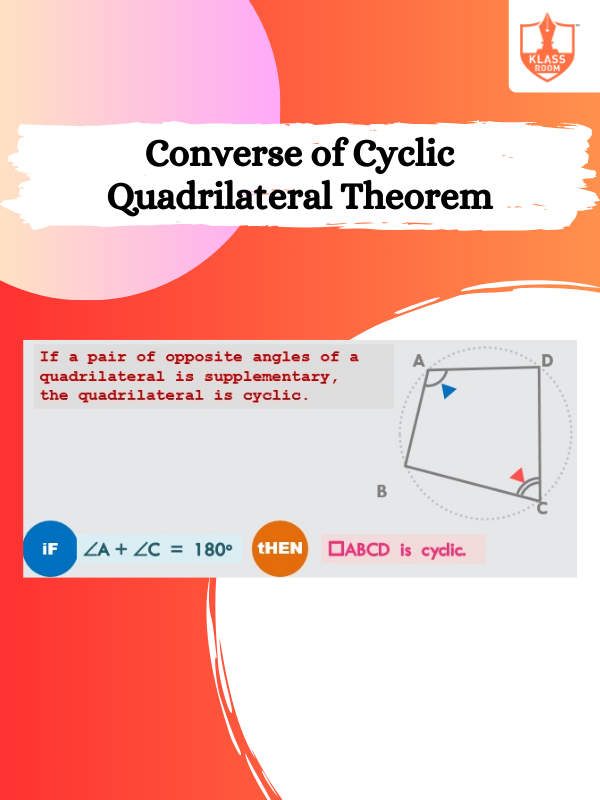
Converse of Cyclic Quadrilateral Theorem
Description: If opposite angles sum to 180°, the quadrilateral can be inscribed in a circle.
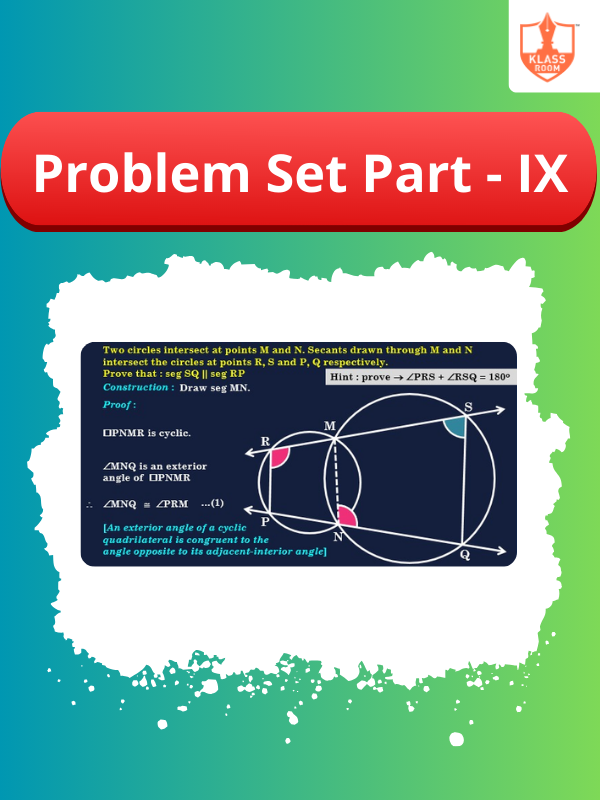
Problem Set Part - IX
Description: Solution of Problem Set Part - IX

Concyclic Points
Description: Concyclic points lie on the same circle, sharing a common circumcircle in a geometric plane.
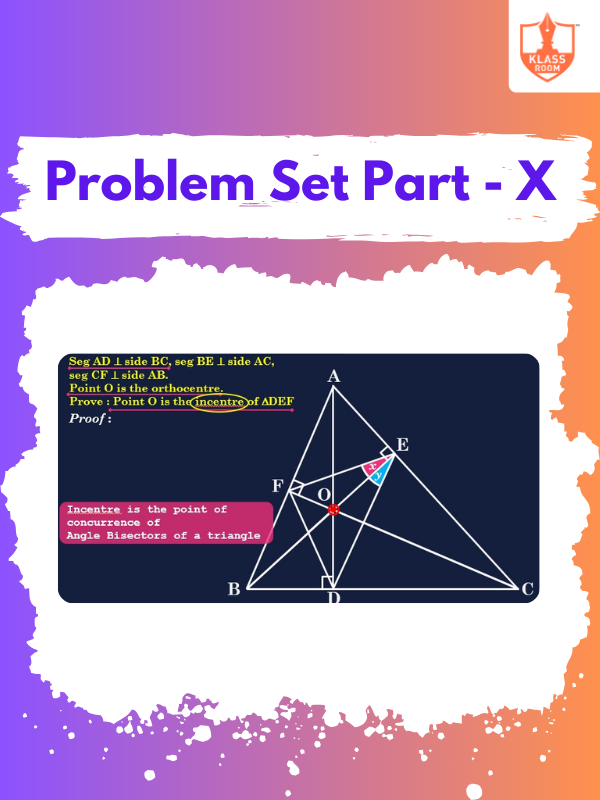
Problem Set Part - X
Description: Solution of Problem Set Part - X
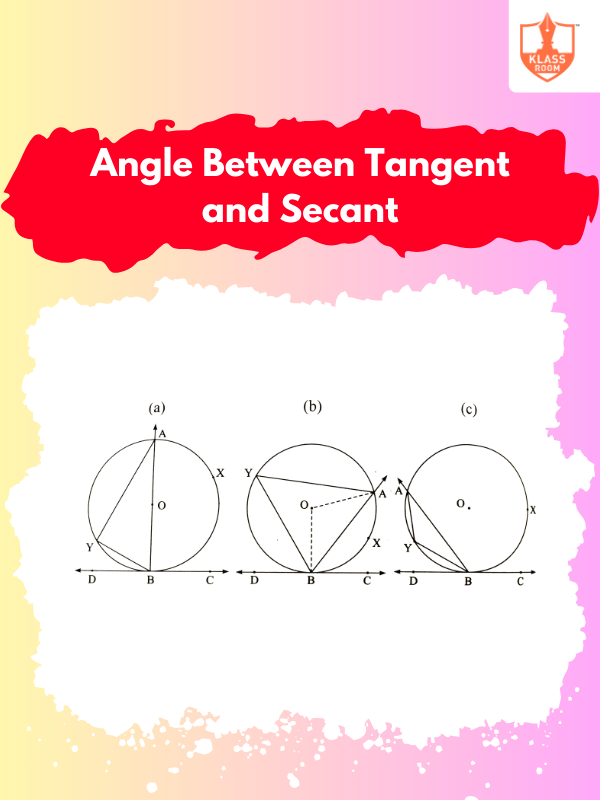
Angle Between Tangent and Secant
Description: The angle between a tangent and secant equals half the intercepted arc's difference.

Problem Set Part - XI
Description: Solution of Problem Set Part - XI

Problem Set Part - XII
Description: Solution of Problem Set Part - XII
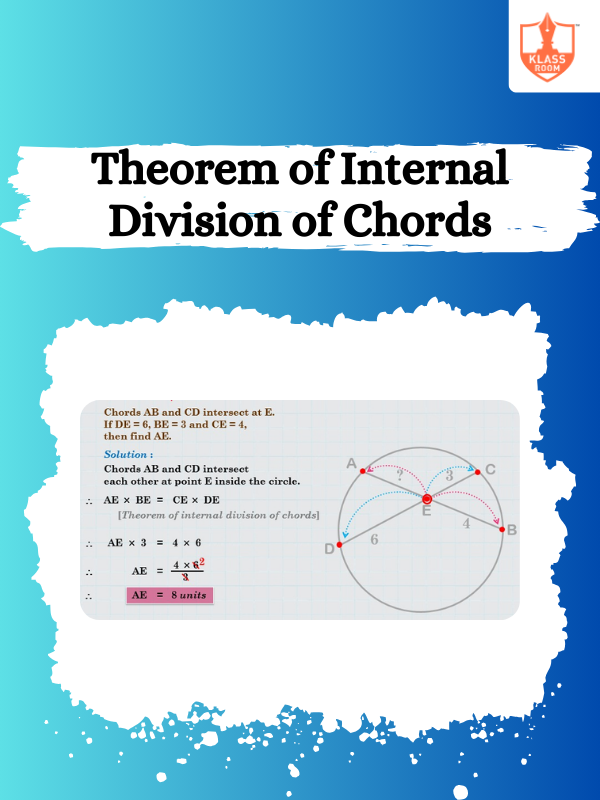
Theorem of Internal Division of Chords
Description: A chord's internal division forms equal ratios of segments, maintaining proportionality along intersecting lines.

Practice Set 3.4 Part VI
Description: Solution of Practice Set 3.4 Part VI

Problem Set Part - XIII
Description: Solution of Problem Set Part - XIII
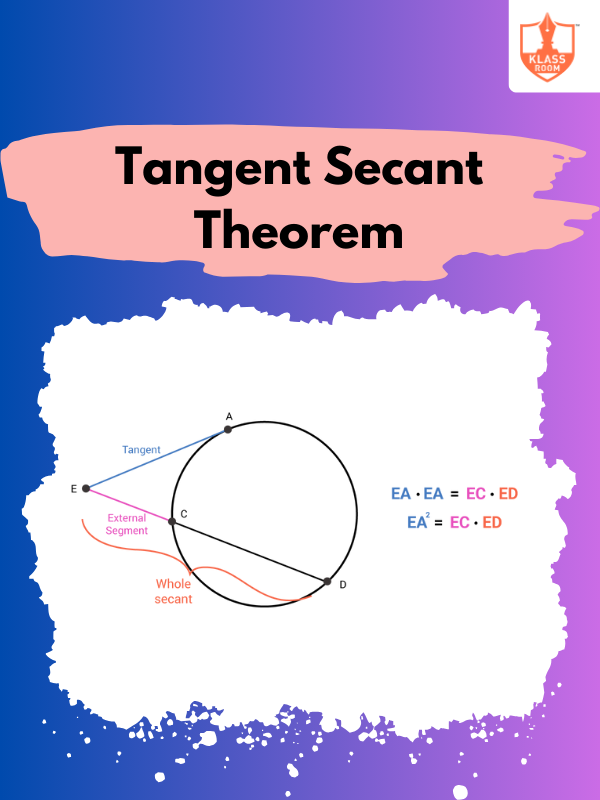
Tangent Secant Theorem
Description: The Tangent Secant Theorem states: tangent² equals the product of external and full secant segments.

Practice Set 3.5
Description: Solution of Practice Set 3.5