Contents

Concept of Current
Description: Current is the flow of electric charge through a conductor, measured in amperes, driven by voltage difference or electromotive force.
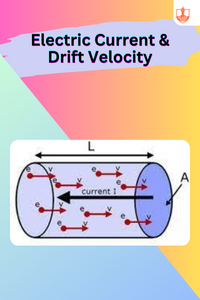
Electric Current & Drift Velocity
Description: Electric current is directly proportional to the drift velocity of charge carriers in a conductor
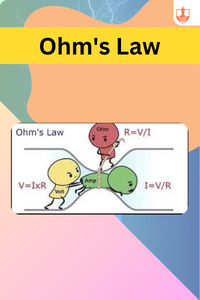
Ohm's Law
Description: Ohm's Law states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across it, given a constant resistance.

Ohmic & Non-ohmic Conductor
Description: Ohmic conductors follow Ohm's Law with constant resistance, while non-Ohmic conductors don't exhibiting variable resistance with changing voltage.
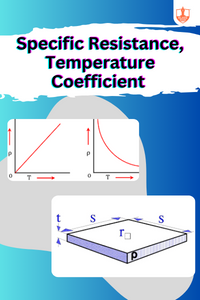
Specific Resistance, Temperature Coefficient
Description: Specific resistance, or resistivity, is a material's intrinsic resistance to current flow, while temperature coefficient indicates how resistance changes with temperature.