Contents

Darwins Theory of Evolution
Description: Darwin's theory of evolution proposes natural selection as the mechanism driving the gradual change and adaptation of species over time

Industrial Melanism
Description: Industrial melanism is the adaptation of organisms to dark coloration in polluted environments, driven by natural selection for camouflage
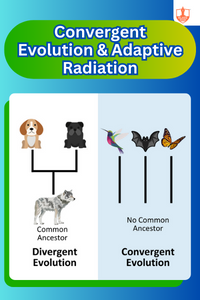
Convergent Evolution & Adaptive Radiation
Description: Convergent evolution: unrelated species evolve similar traits due to similar environmental pressures. Adaptive radiation: rapid diversification of species into different ecological niches.

Common Diseases in Humans
Description: Common human diseases include cardiovascular diseases, respiratory infections, cancer, diabetes, and mental health disorders, impacting individuals worldwide across ages.

Immunity
Description: Immunity is the body's defense system against pathogens, involving white blood cells, antibodies, and memory cells for long-term protection.
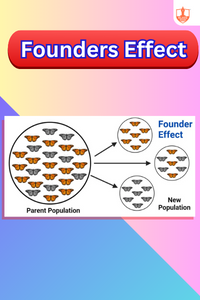
Founders Effect
Description: Founder effect: genetic drift in small population founding a new colony, leading to reduced genetic diversity. Bottleneck effect: population drastically reduced.
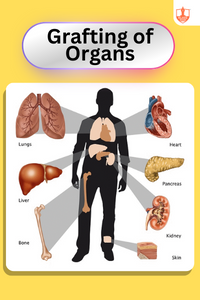
Grafting of Organs
Description: Organ grafting involves transplanting organs from a donor to a recipient to replace damaged or failing organs, often saving lives.

Principles of Biotechnology
Description: Biotechnology uses biological systems, organisms, or their derivatives to develop products and technologies for various fields, including medicine and agriculture.

Agricultural Biotechnology
Description: Agricultural biotechnology applies genetic engineering and molecular biology to improve crop yield, resistance to pests, and nutritional content for agriculture.

Biotechnology In medicinal Field
Description: Biotechnology in medicine uses genetic engineering and bioprocessing to develop drugs, vaccines, and therapies for treating diseases and improving healthcare.

PCR & Genetic Engineering
Description: PCR amplifies DNA segments in vitro. Genetic engineering manipulates DNA to create organisms with desired traits for various applications.
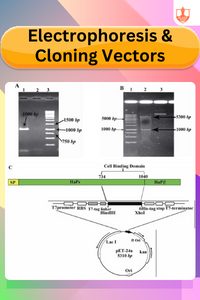
Electrophoresis & Cloning Vectors
Description: Electrophoresis separates DNA fragments by size. Cloning vectors are DNA molecules used to carry foreign DNA into host cells for replication.

Origin of Life & Theories of Evolution
Description: The origin of life involves abiogenesis, where life arises from non-living matter, possibly through chemical evolution in primordial environments.


.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)
.png)


.png)
.png)