Contents
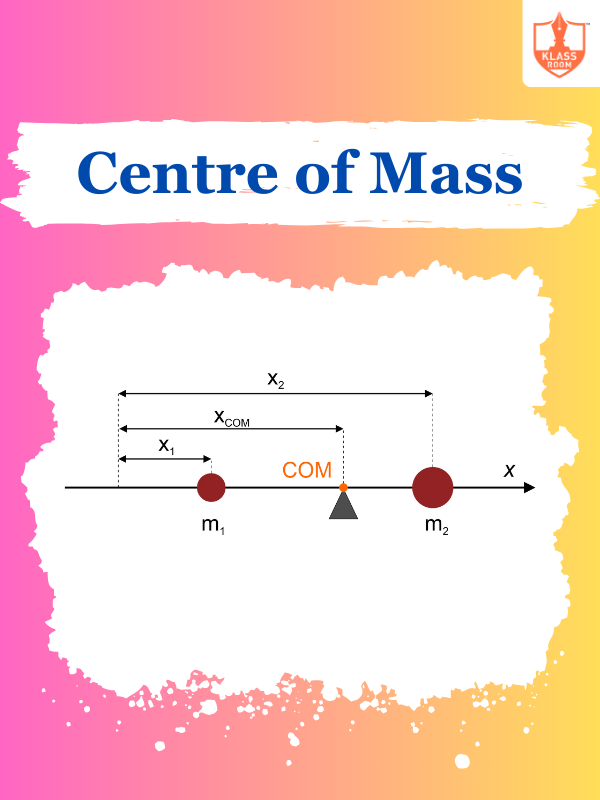
Centre of Mass
Description: Centre of mass is the point where the total mass of a system is concentrated.
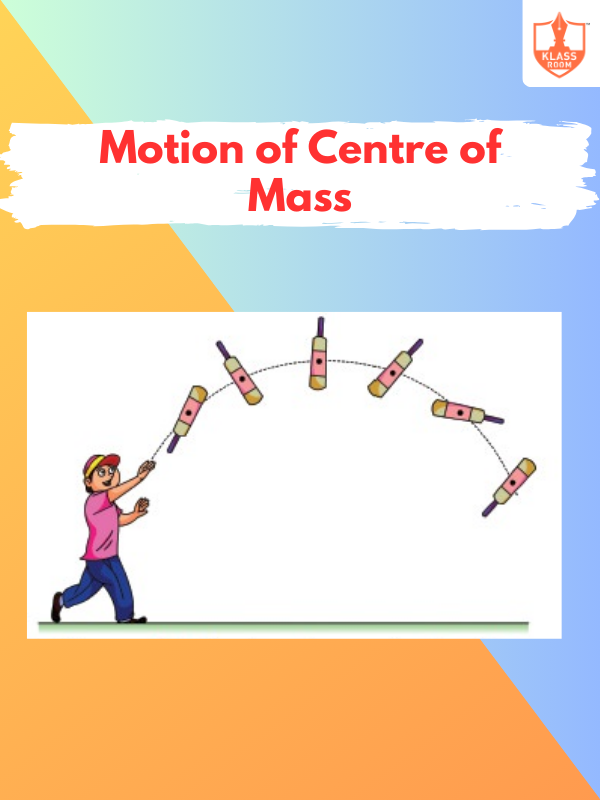
Motion of Centre of Mass
Description: The motion of the center of mass follows the path determined by external forces on the system.
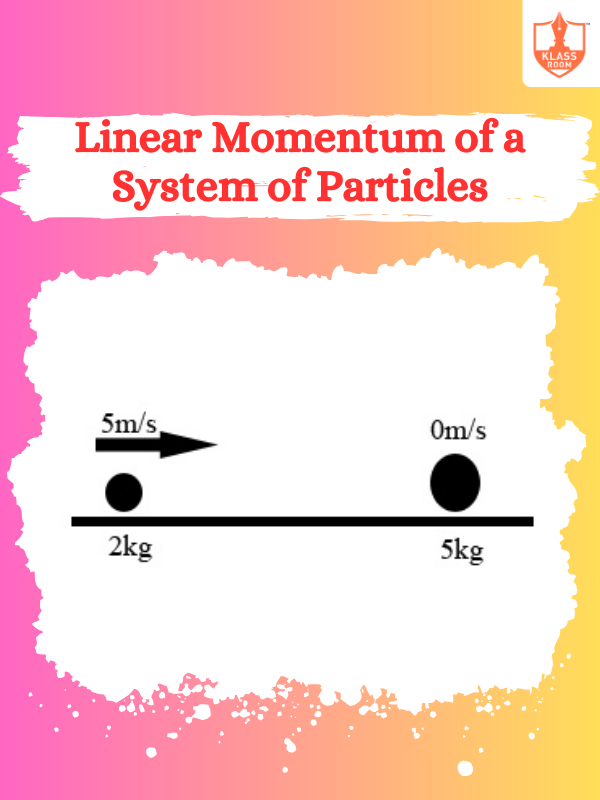
Linear Momentum of a System of Particles
Description: Linear momentum of a system is the vector sum of individual momenta of all particles.
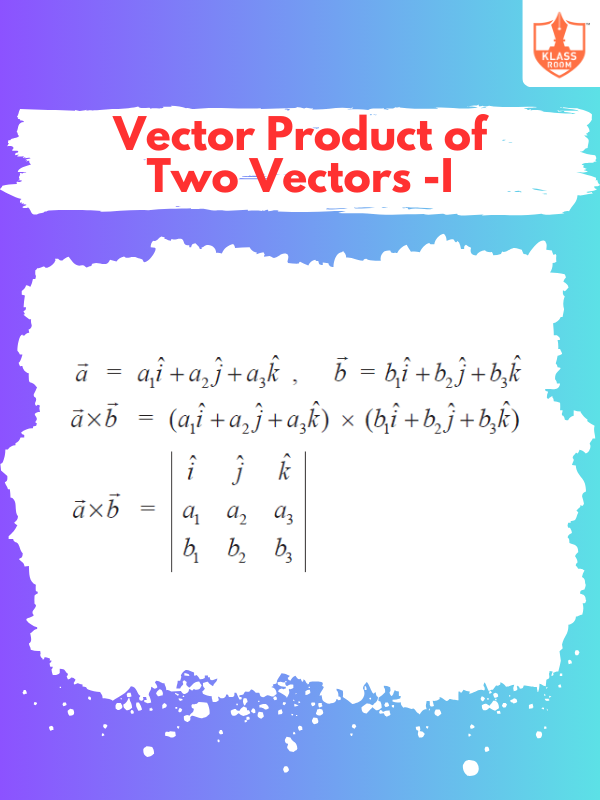
Vector Product of Two Vectors -I
Description: The vector product of two vectors yields a vector perpendicular to both, with magnitude and direction.
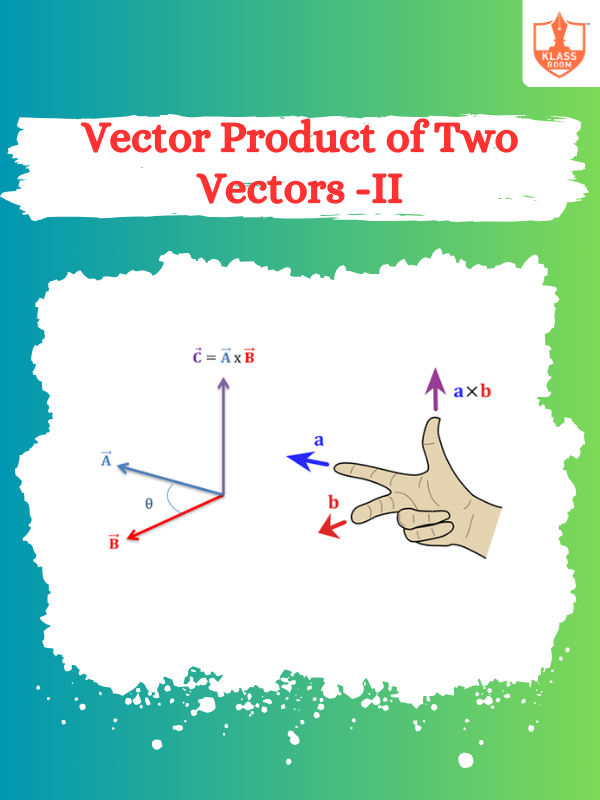
Vector Product of Two Vectors -II
Description: The vector product results in a vector perpendicular to both original vectors, with specific direction.
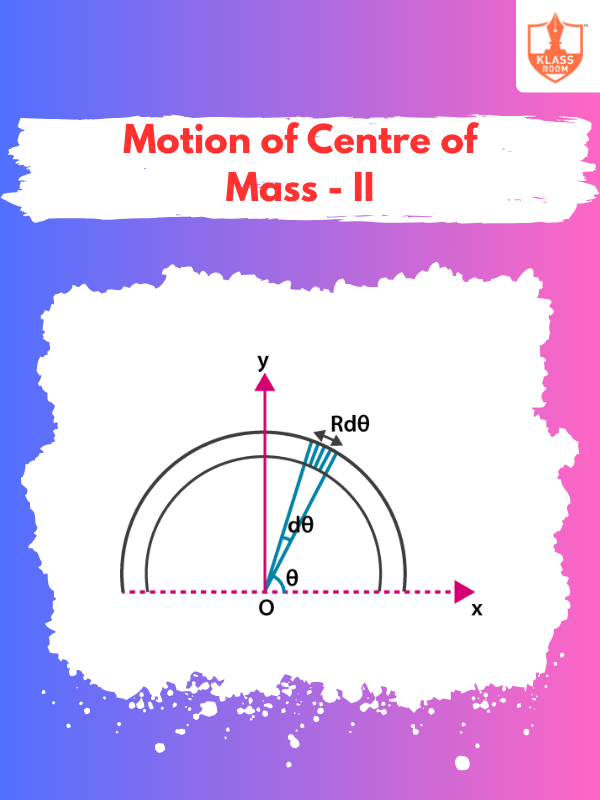
Motion of Centre of Mass - II
Description: Motion of Center of Mass II: Describes mass movement in multi-body systems, focusing on interactions.
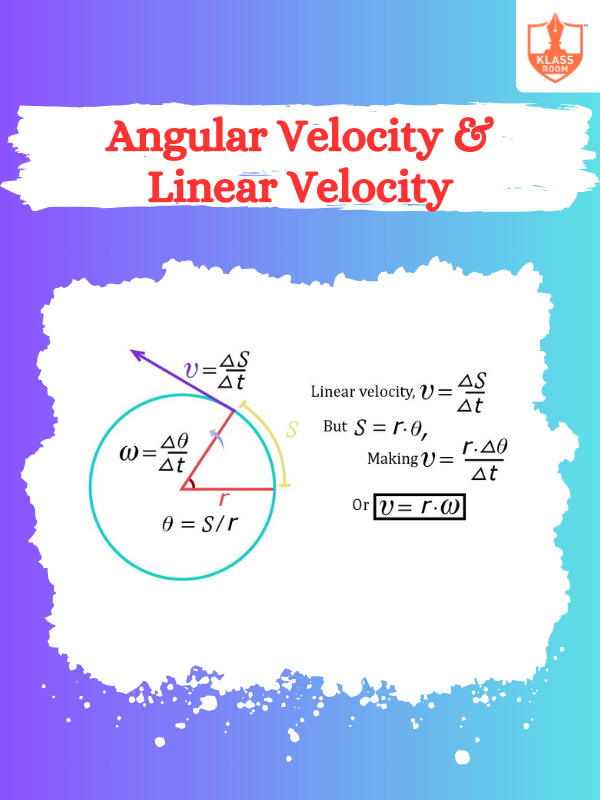
Angular Velocity & Linear Velocity
Description: Angular Velocity: Rotational speed around an axis. Linear Velocity: Straight-line speed of an object.
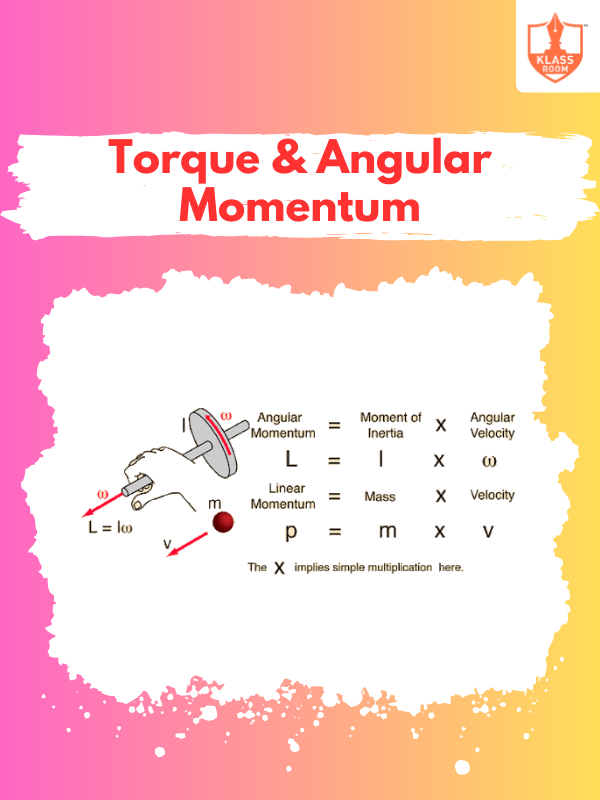
Torque & Angular Momentum
Description: Torque: Force causing rotation. Angular Momentum: Rotational equivalent of linear momentum, conserved in closed systems.
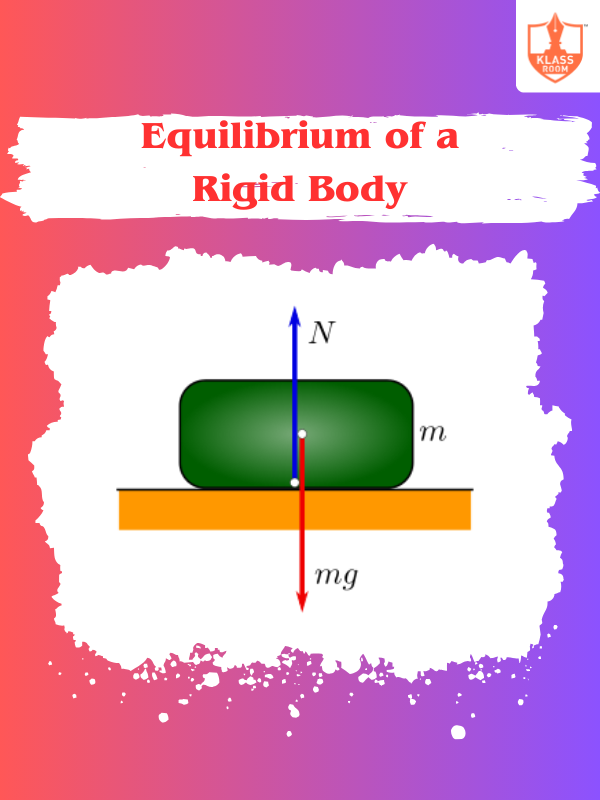
Equilibrium of a Rigid Body
Description: Equilibrium of a Rigid Body: Forces and torques balance, causing no linear or rotational motion.
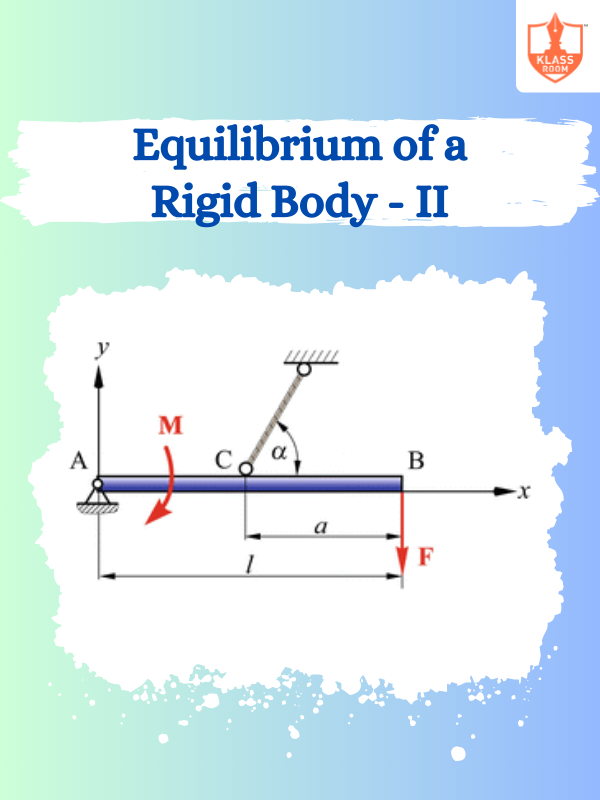
Equilibrium of a Rigid Body - II
Description: Equilibrium of a Rigid Body II: Analyzes conditions for multiple forces and torques in complex systems.
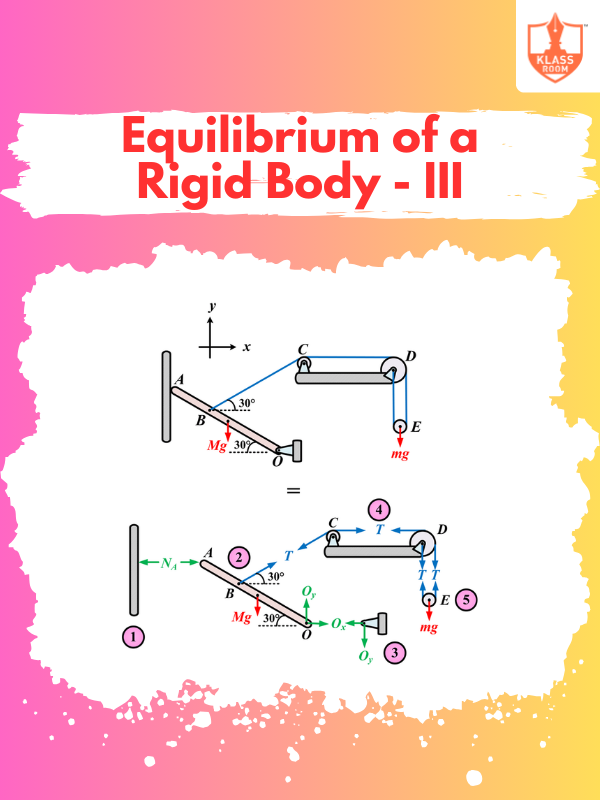
Equilibrium of a Rigid Body - III
Description: Equilibrium of a rigid body means forces and torques balance out, preventing any motion or rotation.
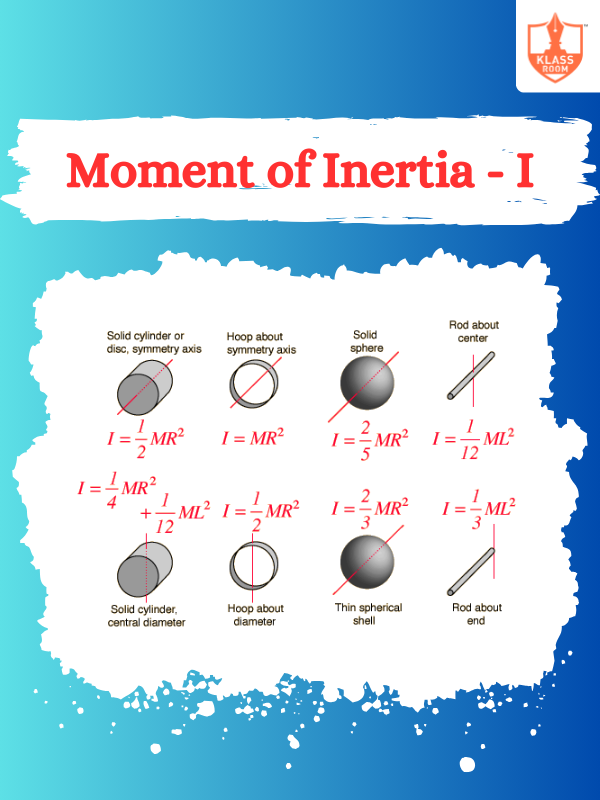
Moment of Inertia - I
Description: Moment of inertia measures an object's resistance to rotational motion about a specific axis.
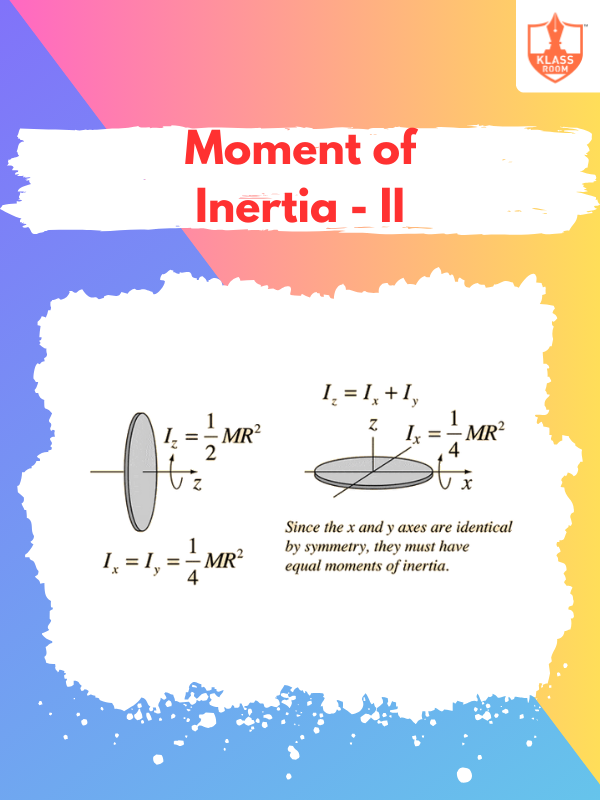
Moment of Inertia - II
Description: Moment of inertia depends on mass distribution relative to the rotation axis, affecting rotational dynamics.
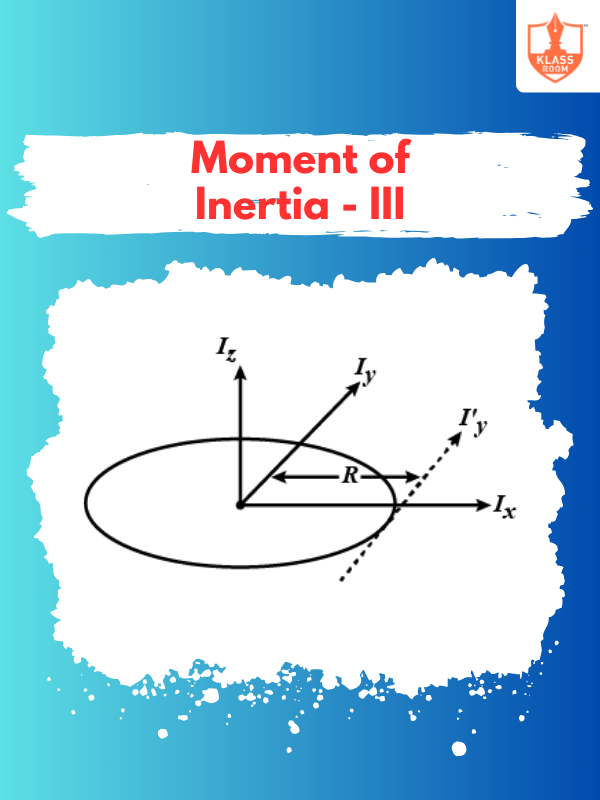
Moment of Inertia - III
Description: Moment of inertia quantifies how mass distribution affects an object's resistance to rotational acceleration.
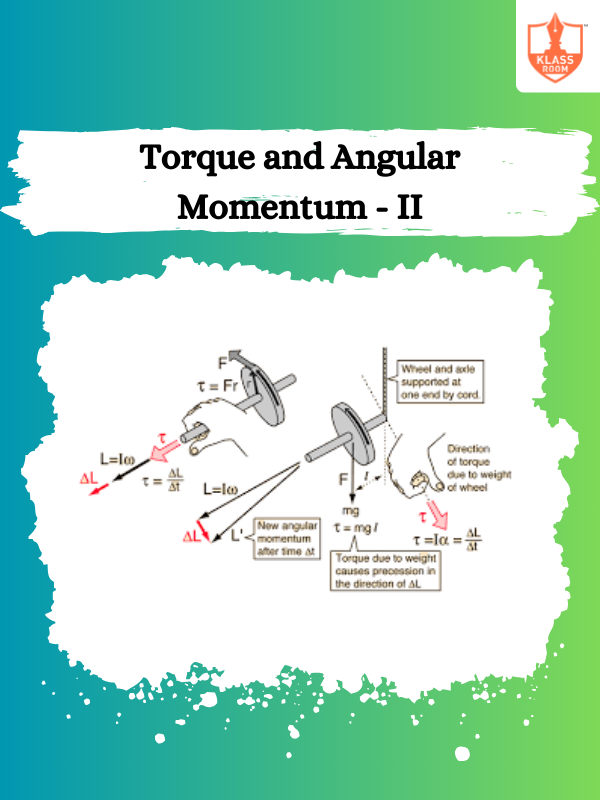
Torque and Angular Momentum - II
Description: Torque causes rotational motion, while angular momentum measures rotational motion’s quantity, depending on mass and velocity.
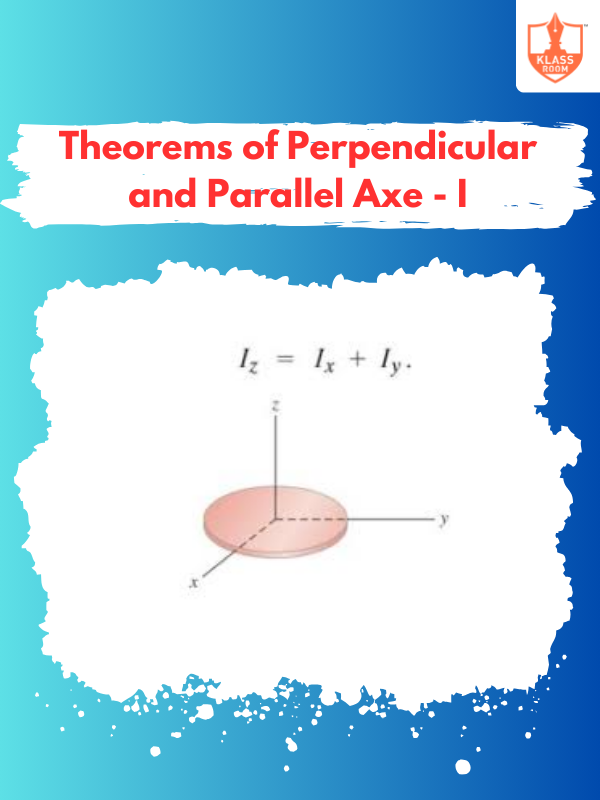
Theorems of Perpendicular and Parallel Axe - I
Description: Theorems of perpendicular and parallel axes relate to moments of inertia in rotating rigid bodies.
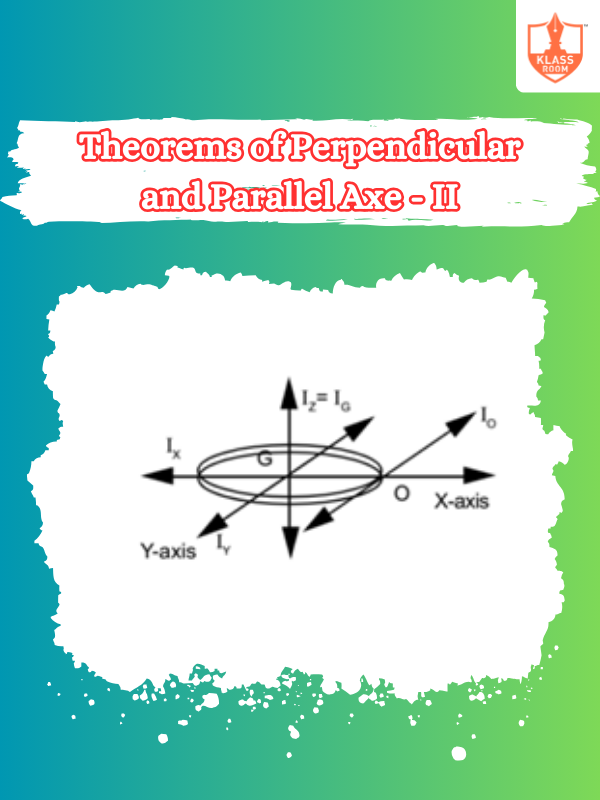
Theorems of Perpendicular and Parallel Axe - II
Description: These theorems extend to calculating moments of inertia about shifted axes in complex systems.
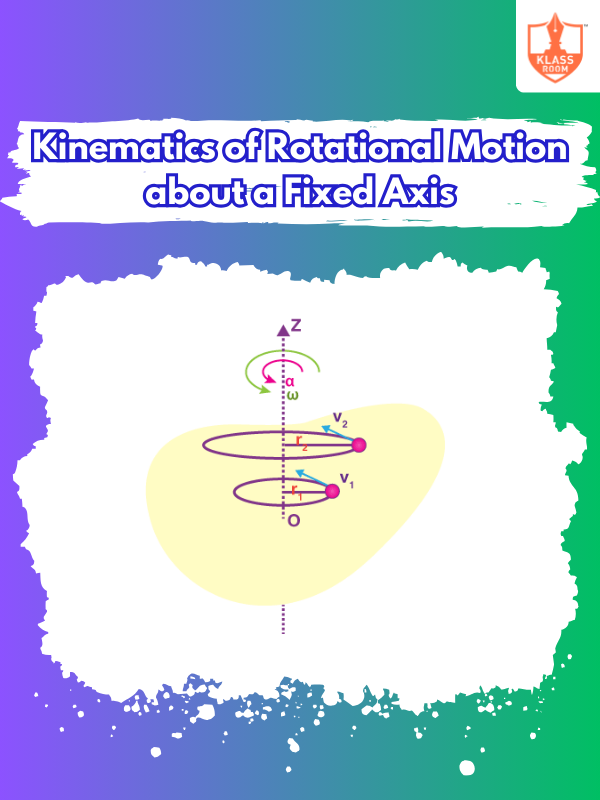
Kinematics of Rotational Motion about a Fixed Axis
Description: It studies the angular motion of objects around a fixed axis, involving angular velocity and acceleration.
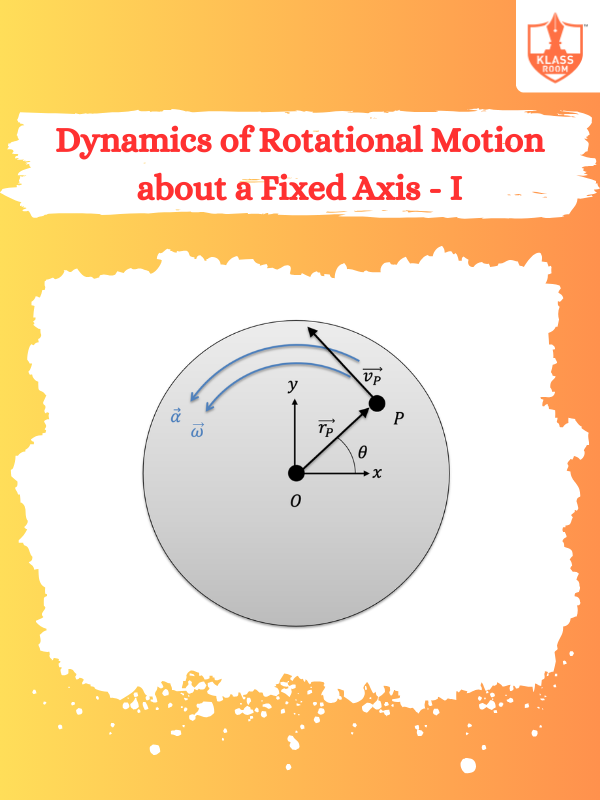
Dynamics of Rotational Motion about a Fixed Axis - I
Description: It explores torque, angular momentum, and rotational energy in objects rotating about a fixed axis.
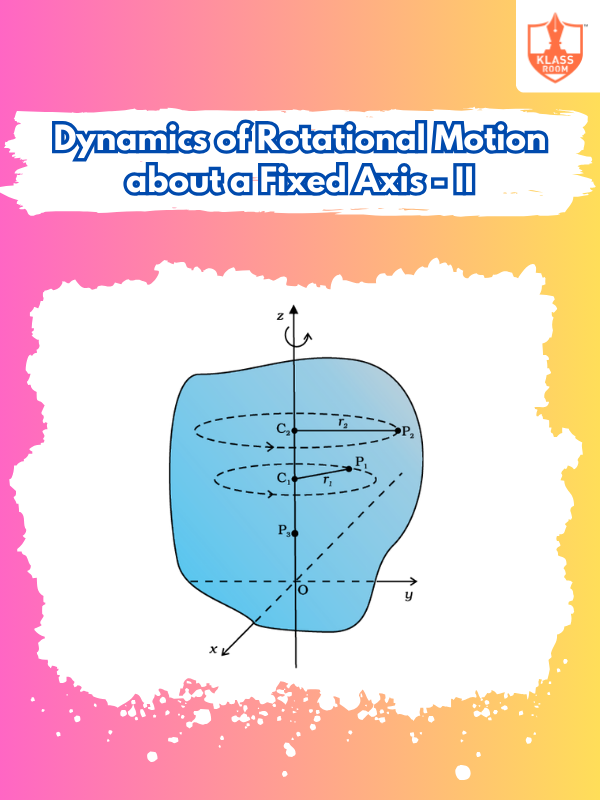
Dynamics of Rotational Motion about a Fixed Axis - II
Description: Focuses on equations of motion, involving torque, moment of inertia, and angular acceleration in rotational systems.
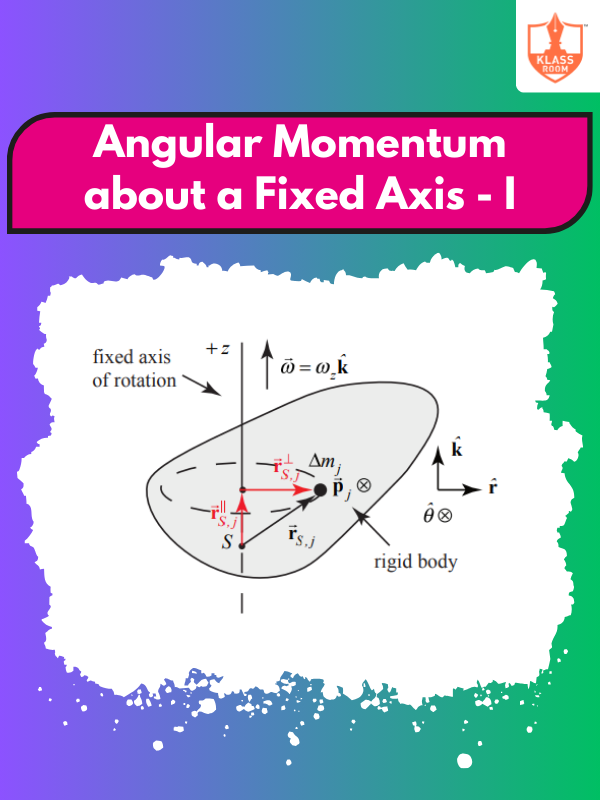
Angular Momentum about a Fixed Axis - I
Description: Angular momentum about a fixed axis depends on the moment of inertia and angular velocity of rotation.
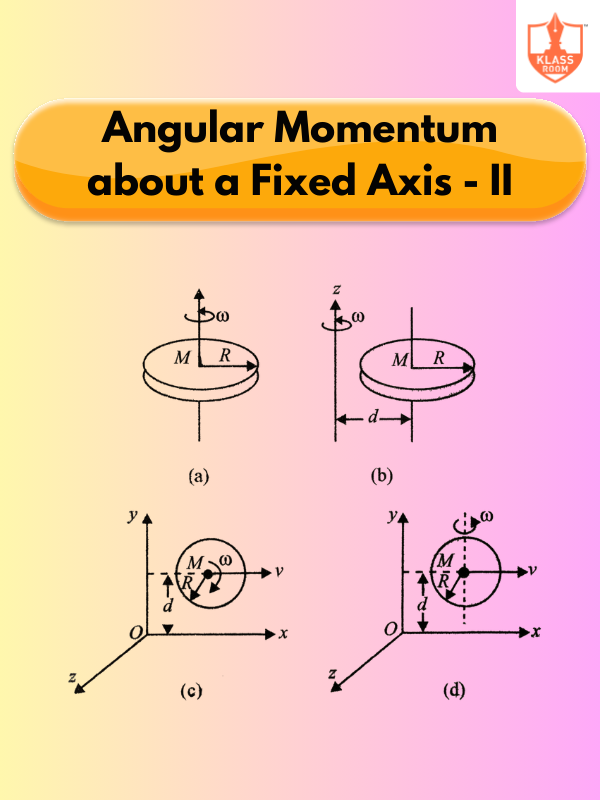
Angular Momentum about a Fixed Axis - II
Description: Conservation of angular momentum states that it remains constant if no external torque acts on the system.
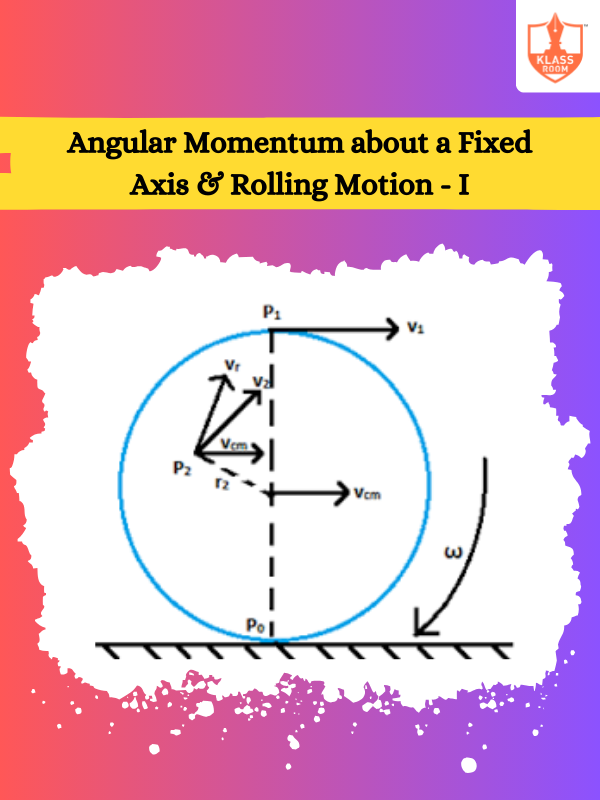
Angular Momentum about a Fixed Axis & Rolling Motion - I
Description: Combines rotational and translational motion, analyzing how angular momentum influences rolling without slipping.
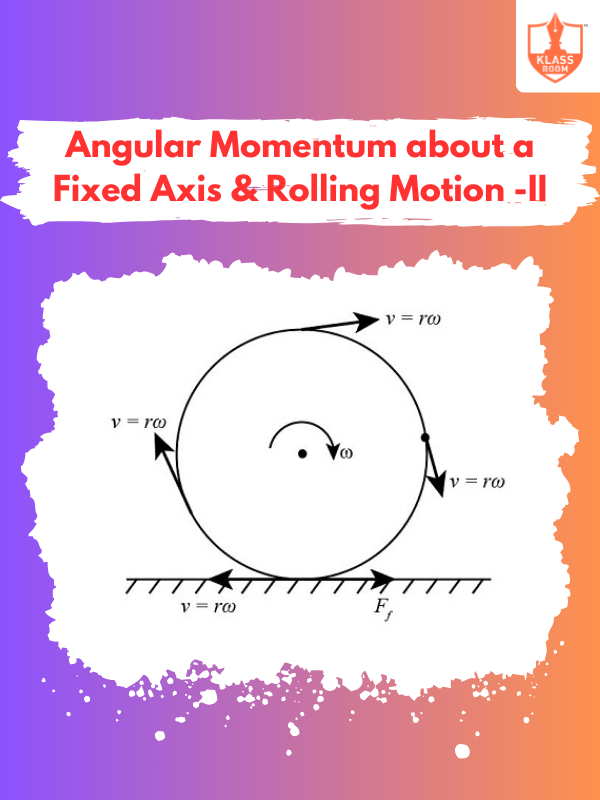
Angular Momentum about a Fixed Axis & Rolling Motion - II
Description: Explores the conservation of angular momentum in rolling motion, focusing on the relationship between rotational and linear velocities.

Angular Momentum about a Fixed Axis & Rolling Motion - III
Description: Investigates energy distribution in rolling motion, balancing rotational kinetic energy and translational kinetic energy.
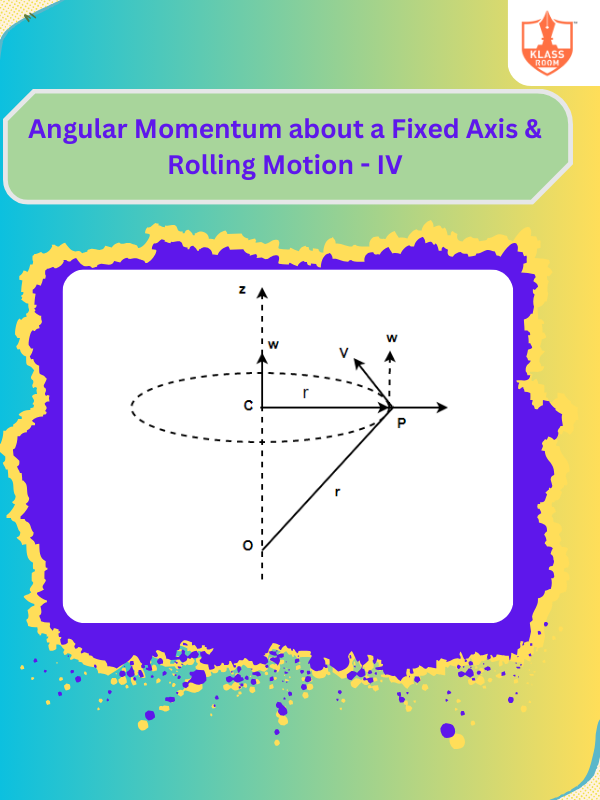
Angular Momentum about a Fixed Axis & Rolling Motion - IV
Description: Angular momentum about a fixed axis involves rotational inertia; rolling motion combines rotation and translation.
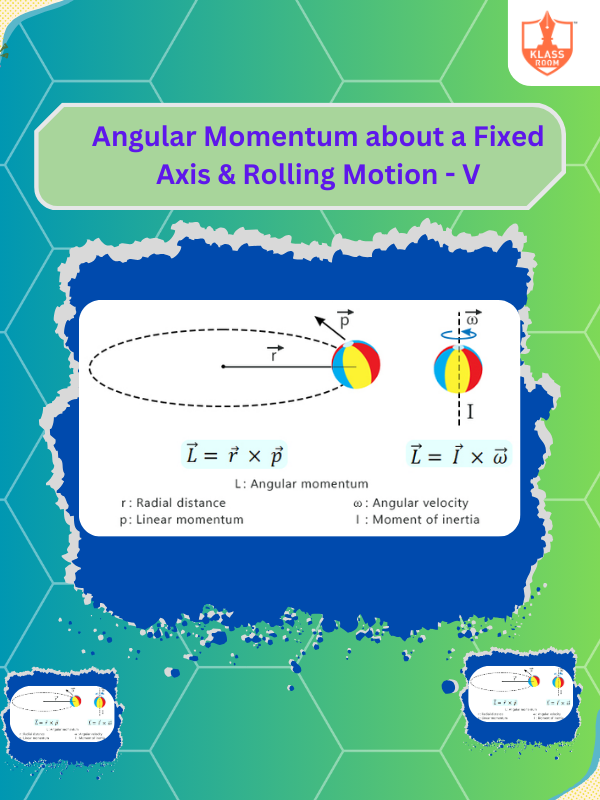
Angular Momentum about a Fixed Axis & Rolling Motion - V
Description: Angular momentum: conserved for a fixed axis; rolling motion links angular velocity with translational speed.
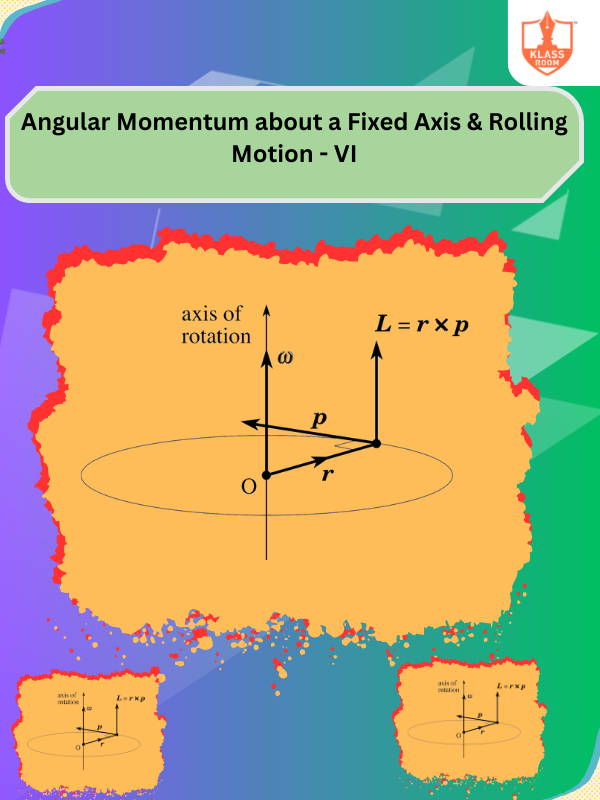
Angular Momentum about a Fixed Axis & Rolling Motion - VI
Description: Angular momentum depends on rotational inertia and angular velocity; rolling motion involves no slipping conditions.
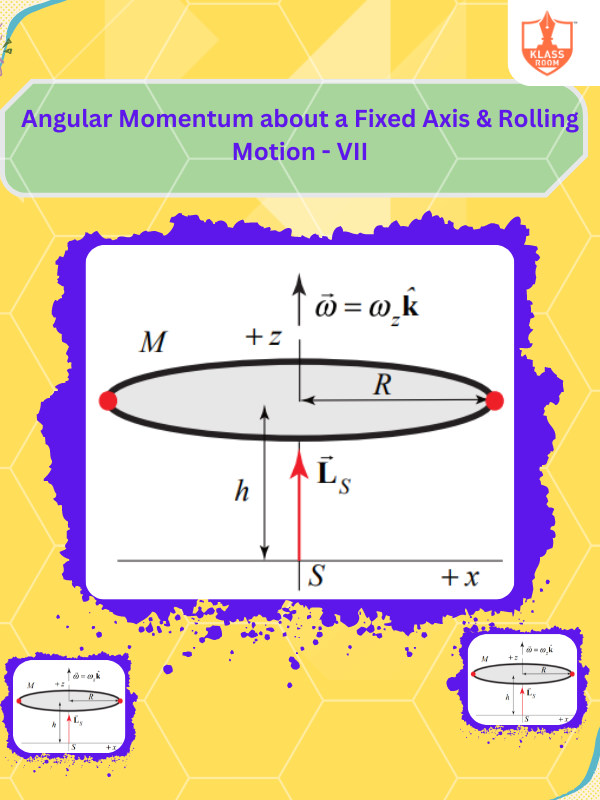
Angular Momentum about a Fixed Axis & Rolling Motion - VII
Description: Angular momentum around a fixed axis: constant; rolling motion blends rotation and linear displacement.
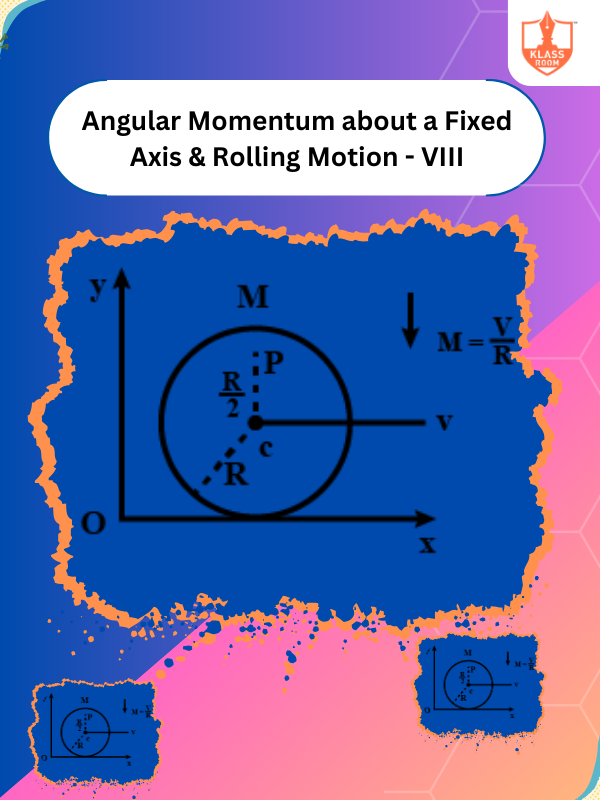
Angular Momentum about a Fixed Axis & Rolling Motion - VIII
Description: Angular momentum conserves rotational motion; rolling motion requires rotational inertia and friction for no slipping.
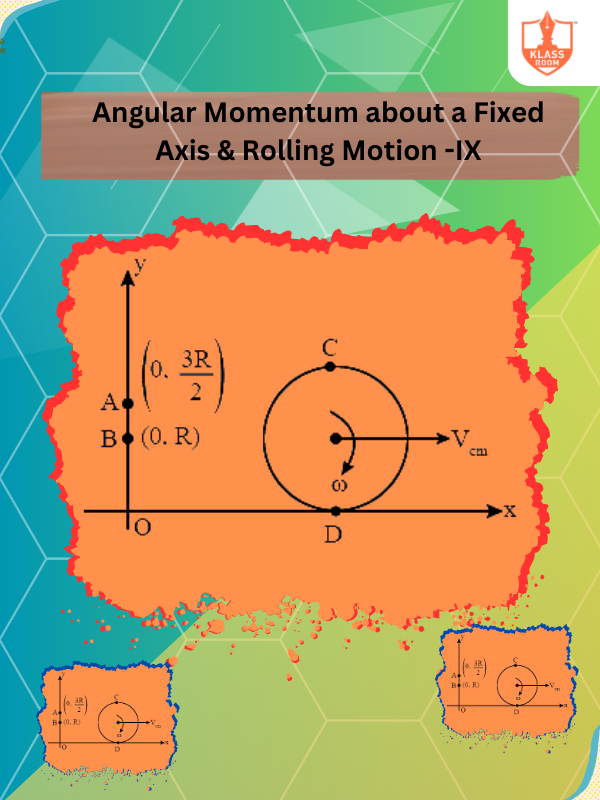
Angular Momentum about a Fixed Axis & Rolling Motion -IX
Description: Angular momentum: product of inertia and angular velocity; rolling motion merges rotational and linear movements.
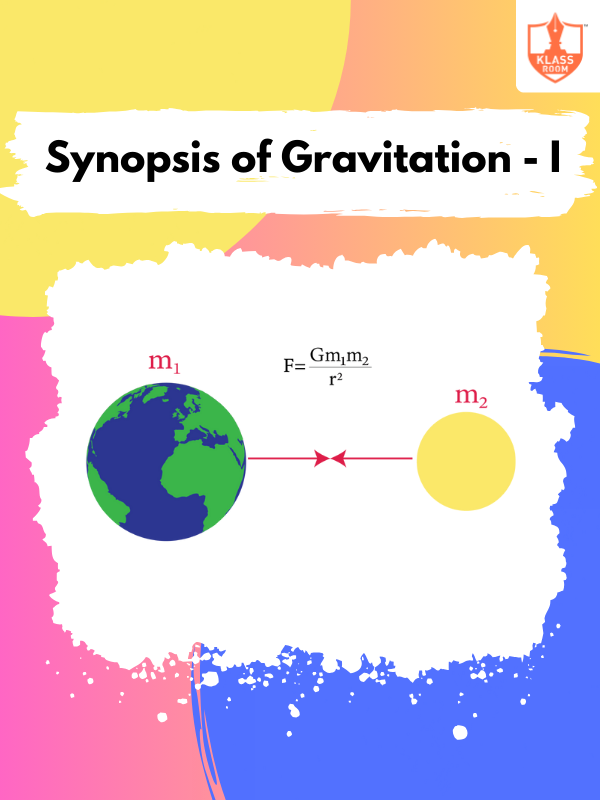
Synopsis of Gravitation - I
Description: Synopsis of Gravitation - I introduces the concept of gravitational force between two masses in space.

Synopsis of Gravitation - II
Description: Synopsis of Gravitation - II explores gravitational potential energy and the influence of gravity on objects.
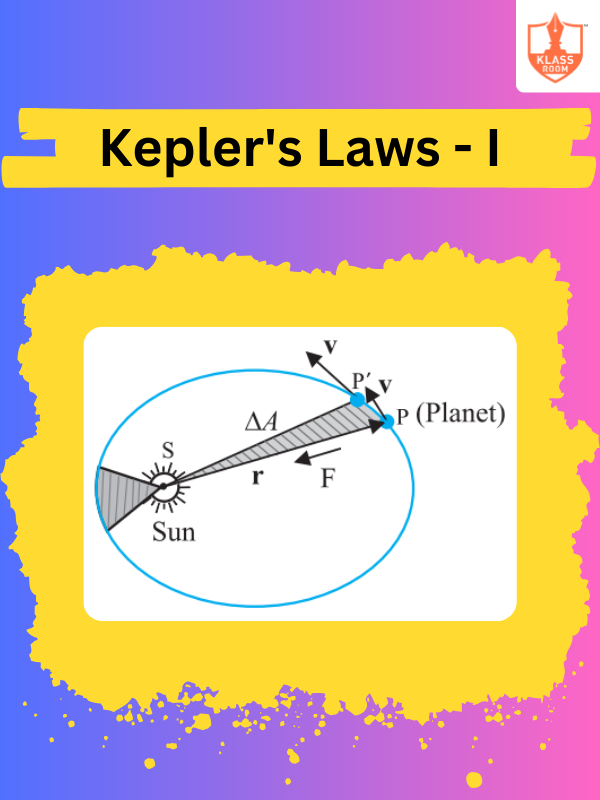
Kepler's Laws - I
Description: Kepler's Laws - I covers the law of planetary orbits, stating planets move in elliptical paths.
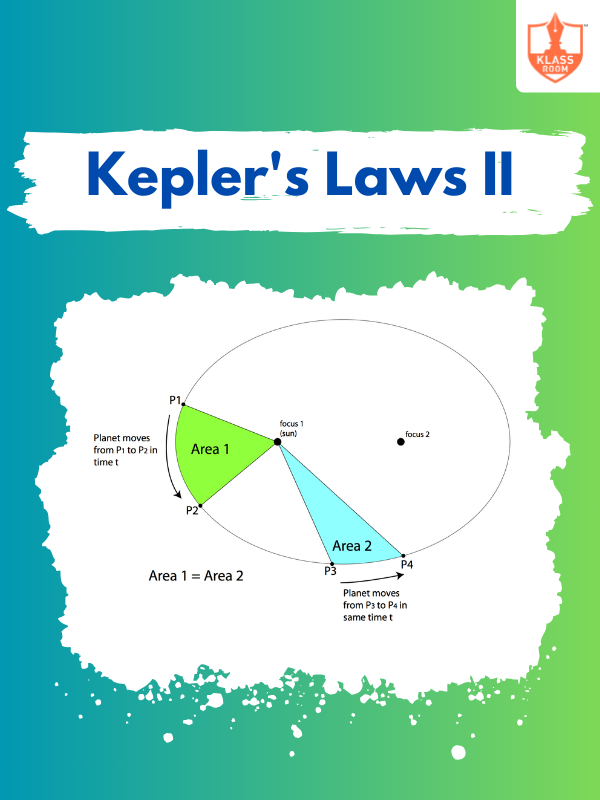
Kepler's Laws II
Description: Kepler's Laws - II explains the law of equal areas, describing the speed of planetary motion.
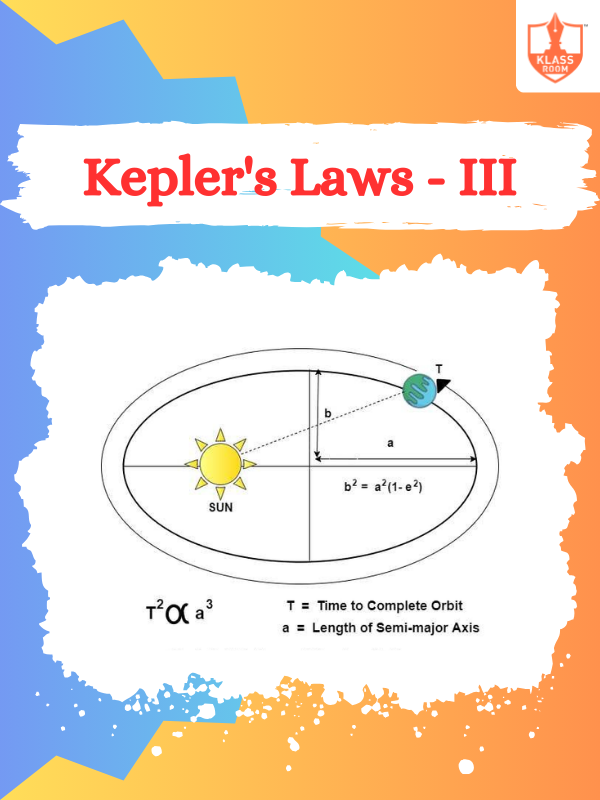
Kepler's Laws - III
Description: Kepler's Laws - III discusses the law of harmonies, relating orbital periods to distances from the Sun.
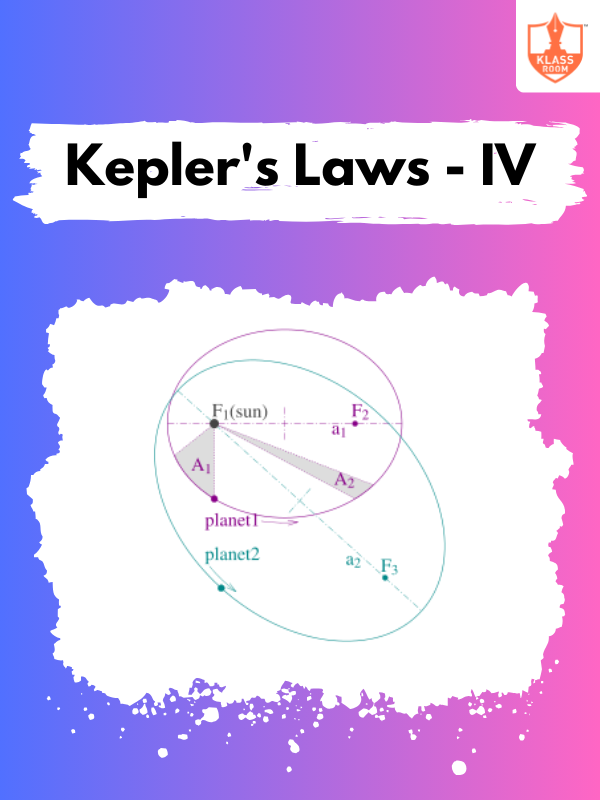
Kepler's Laws - IV
Description: Kepler's Laws - IV elaborates on the mathematical derivations and applications of Kepler’s laws in astronomy.
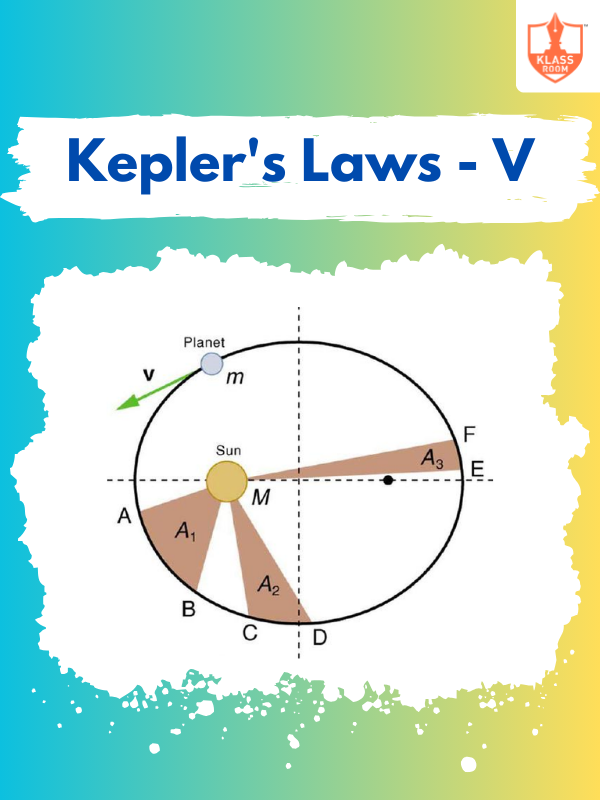
Kepler's Laws - V
Description: Kepler's Laws - V focuses on advanced applications of Kepler's laws in satellite and planetary orbits.
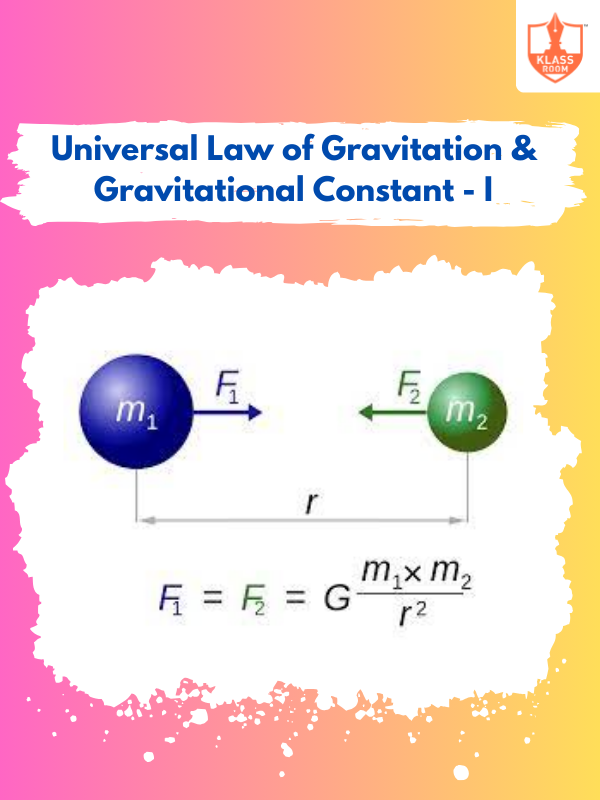
Universal Law of Gravitation & Gravitational Constant - I
Description: Universal Law of Gravitation & Gravitational Constant - I introduces Newton's law of universal gravitation.
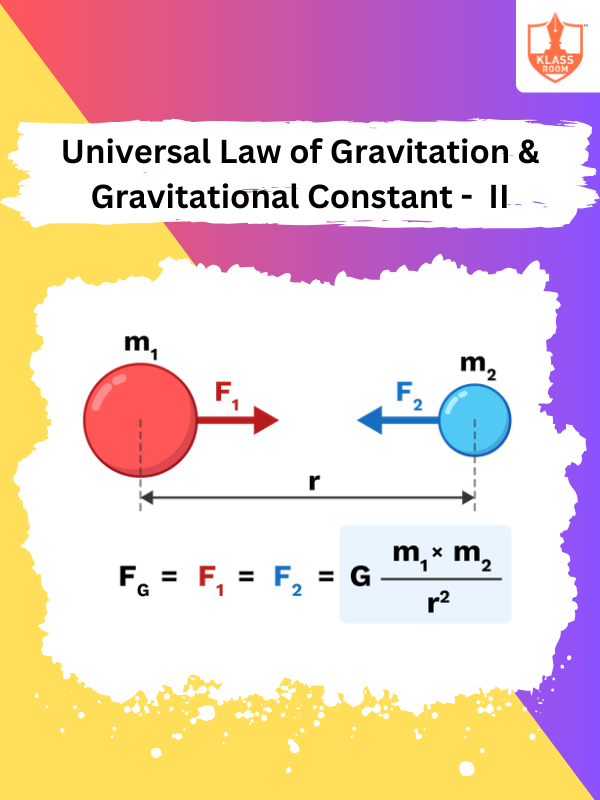
Universal Law of Gravitation & Gravitational Constant - II
Description: Universal Law of Gravitation & Gravitational Constant - II explores the gravitational constant and its role in calculations.
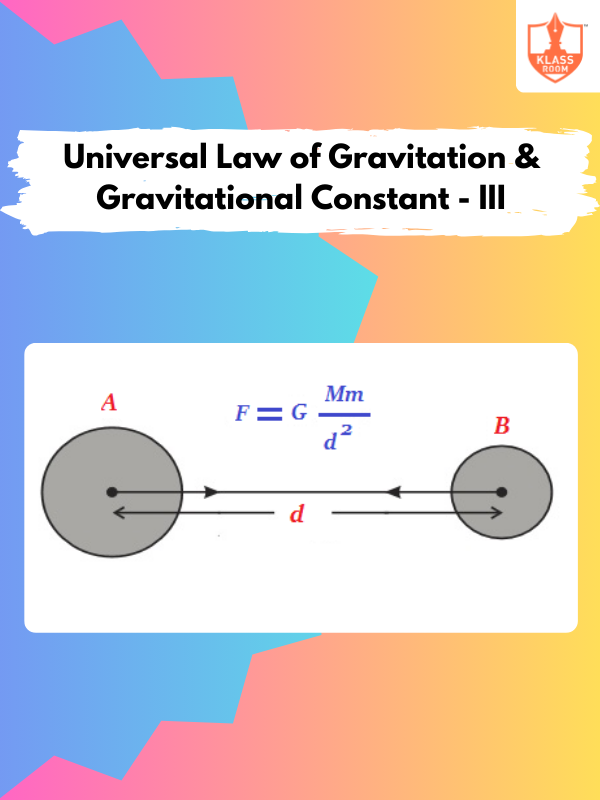
Universal Law of Gravitation & Gravitational Constant - III
Description: Universal Law of Gravitation & Gravitational Constant - III explains the relationship between gravitational force and mass.
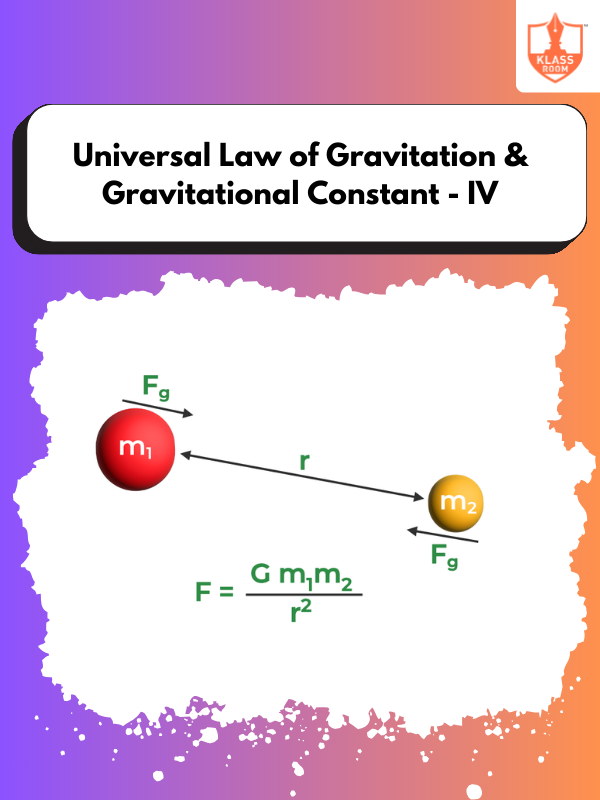
Universal Law of Gravitation & Gravitational Constant - IV
Description: Universal Law of Gravitation & Gravitational Constant - IV discusses how gravity affects objects' motion on Earth.
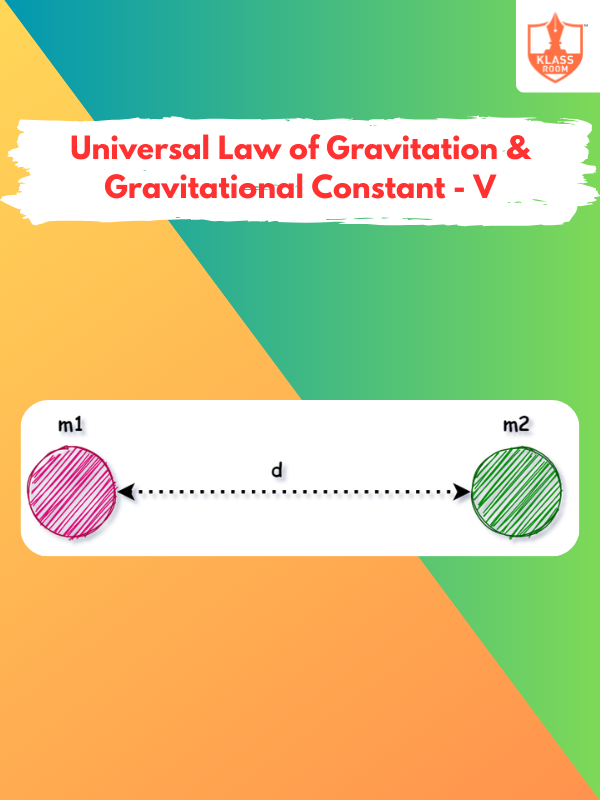
Universal Law of Gravitation & Gravitational Constant - V
Description: Universal Law of Gravitation & Gravitational Constant - V covers calculations involving gravitational potential and kinetic energy.
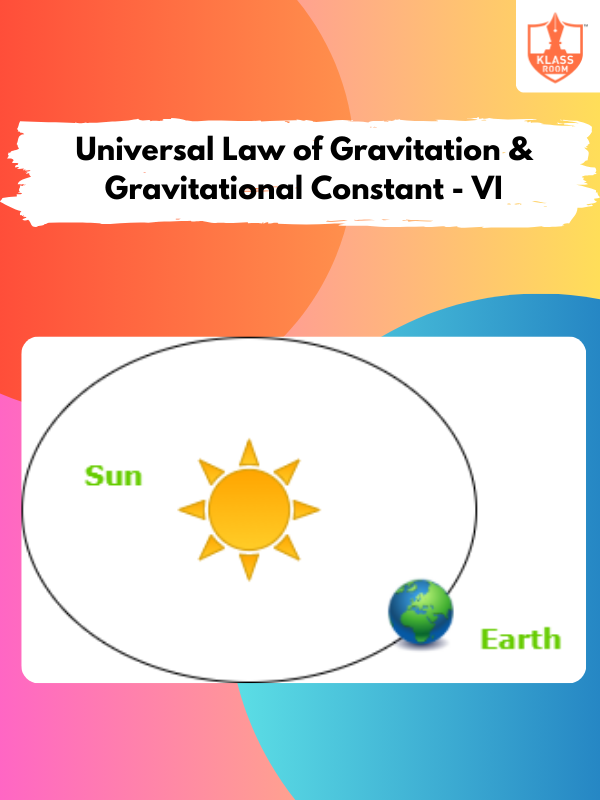
Universal Law of Gravitation & Gravitational Constant - VI
Description: Universal Law of Gravitation & Gravitational Constant - VI explains gravitational fields and their impact on objects' acceleration.
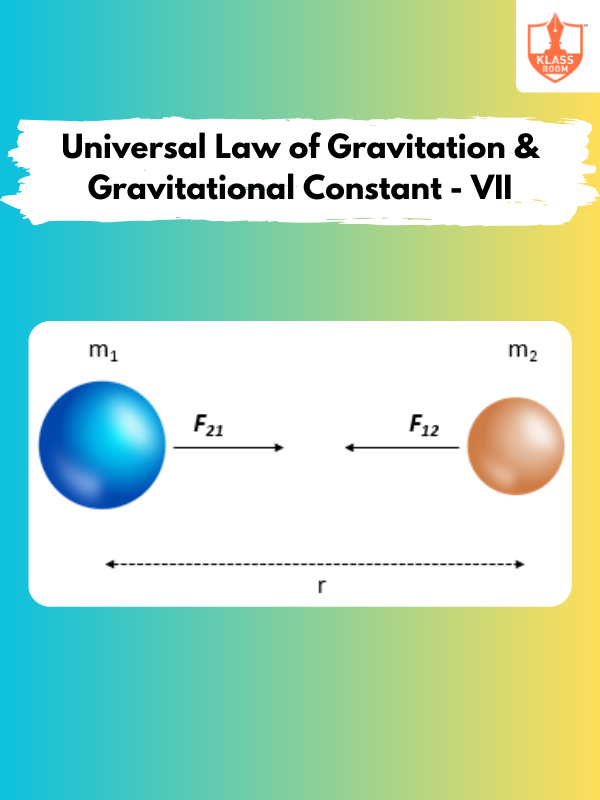
Universal Law of Gravitation & Gravitational Constant - VII
Description: Universal Law of Gravitation & Gravitational Constant - VII discusses experimental validation of the law and gravitational constant.

Acceleration Due to Gravity of the Earth - I
Description: Acceleration Due to Gravity of the Earth - I introduces Earth's gravity and how it affects objects' free-fall acceleration.
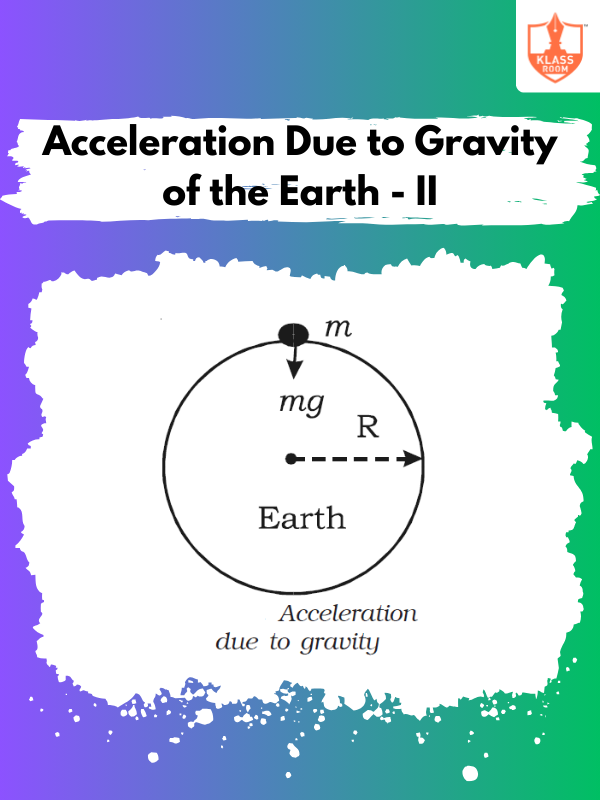
Acceleration Due to Gravity of the Earth - II
Description: Acceleration Due to Gravity of the Earth - I explains Earth's gravitational pull and its effect on falling objects.
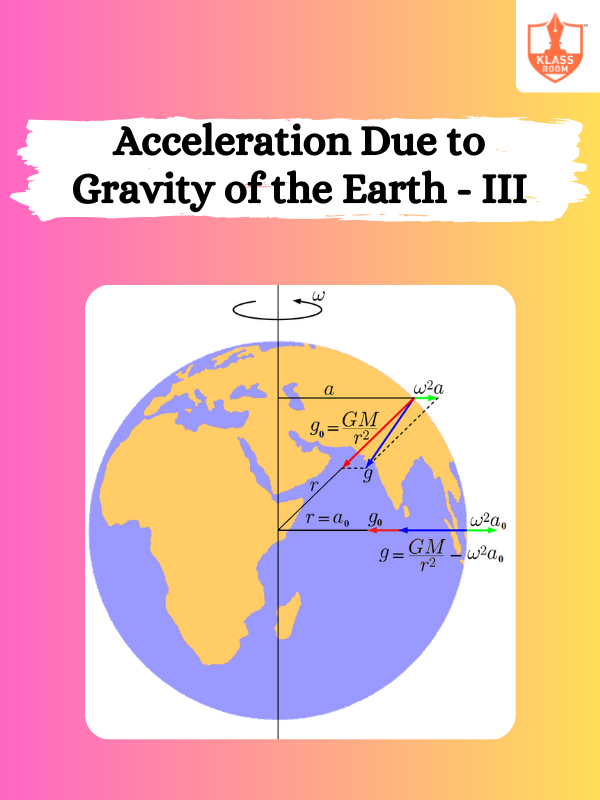
Acceleration Due to Gravity of the Earth - III
Description: Acceleration Due to Gravity of the Earth - II discusses variations in gravity based on altitude and Earth's shape.

Gravitational Potential Energy - I
Description: Gravitational Potential Energy - I introduces potential energy stored due to an object's position in a gravitational field.
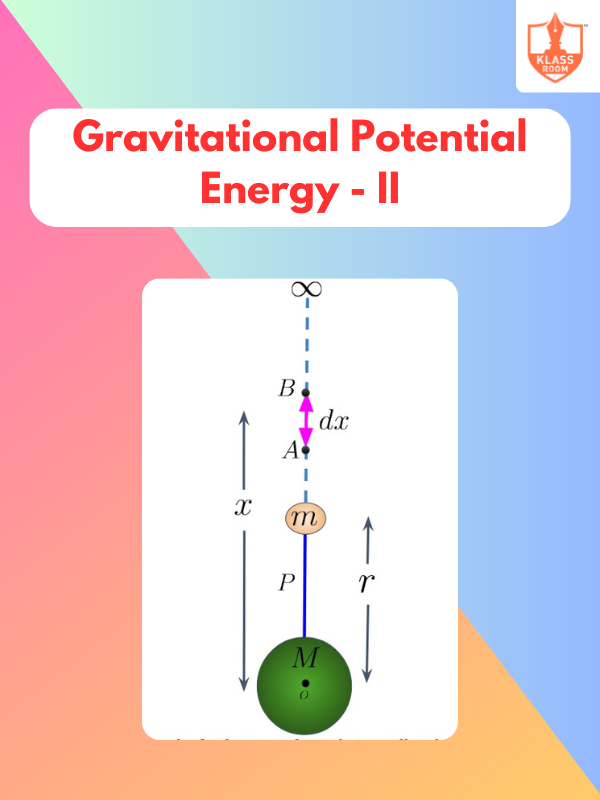
Gravitational Potential Energy - II
Description: Gravitational Potential Energy - II covers the formula for calculating gravitational potential energy between two masses.
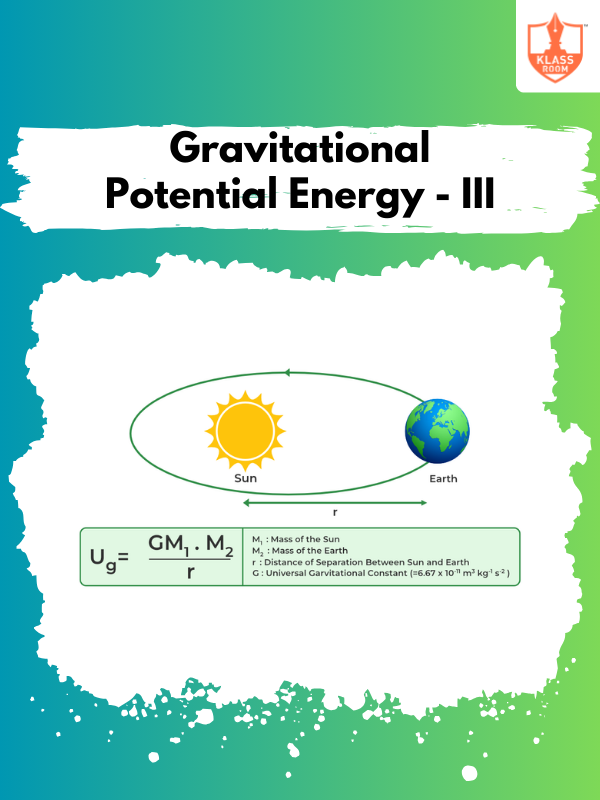
Gravitational Potential Energy - III
Description: Gravitational Potential Energy - III explains how gravitational potential energy changes with distance and mass.
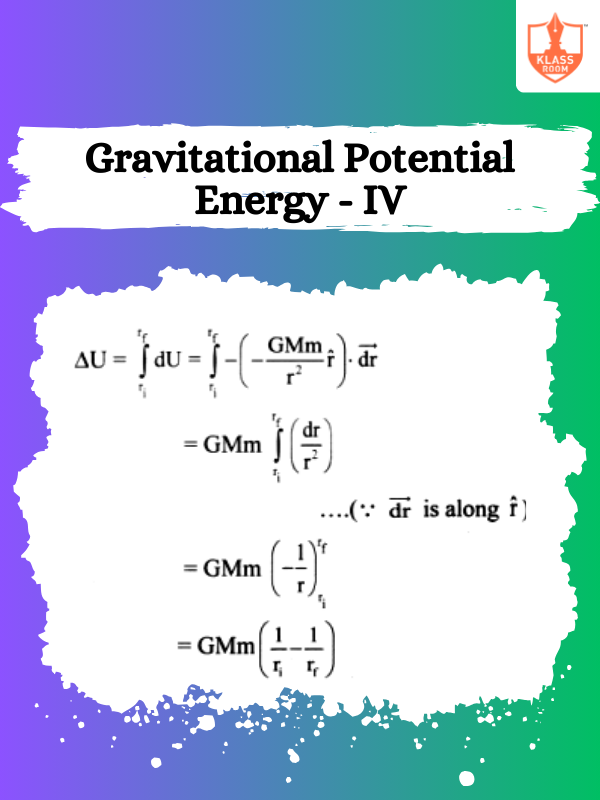
Gravitational Potential Energy - IV
Description: Gravitational Potential Energy - IV explores applications of gravitational potential energy in planetary motion and orbits.

Acceleration due to Gravity Below and Above the Surface of Earth
Description: Acceleration due to Gravity Below and Above the Surface of Earth explains how gravity changes with altitude and depth.
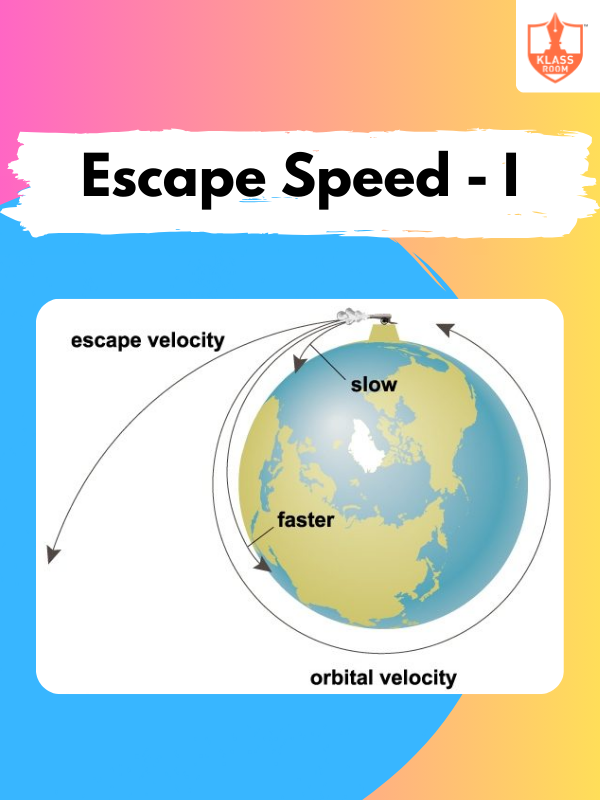
Escape Speed - I
Description: Escape Speed - I introduces the minimum velocity needed for an object to escape Earth's gravitational pull.
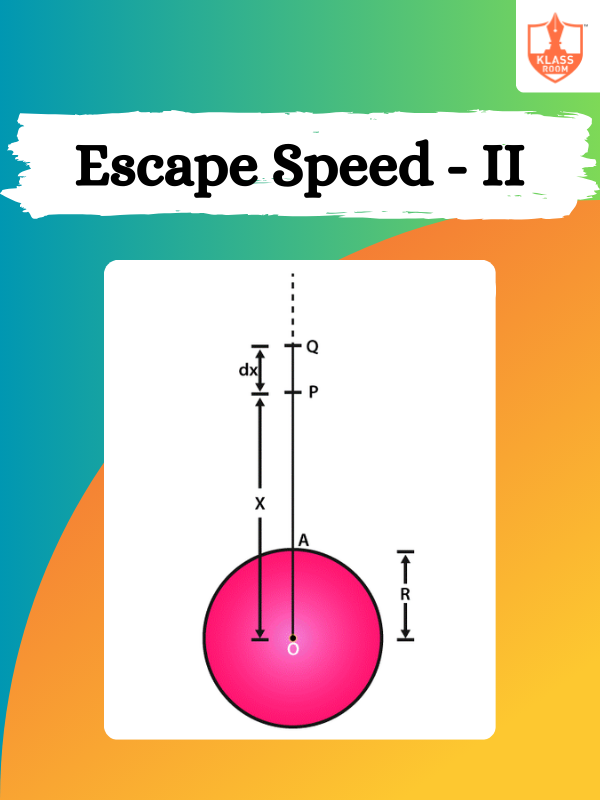
Escape Speed - II
Description: Escape Speed - II covers the mathematical derivation and factors affecting escape speed, like mass and radius.

Escape Speed - III
Description: Escape Speed - III discusses practical examples and applications of escape velocity in space travel.

Earth Satellites - I
Description: Earth Satellites - I introduces artificial satellites and their orbits around Earth for communication, research, and navigation.

Earth Satellites - II
Description: Earth Satellites - II explains satellite types, including geostationary and low-Earth orbits, and their respective functions.

Earth Satellites - III
Description: Earth Satellites - III explores satellite launches, orbital paths, and how satellites stay in motion.

Earth Satellites -IV
Description: Earth Satellites - IV covers advanced applications of Earth satellites in weather monitoring, mapping, and space exploration.
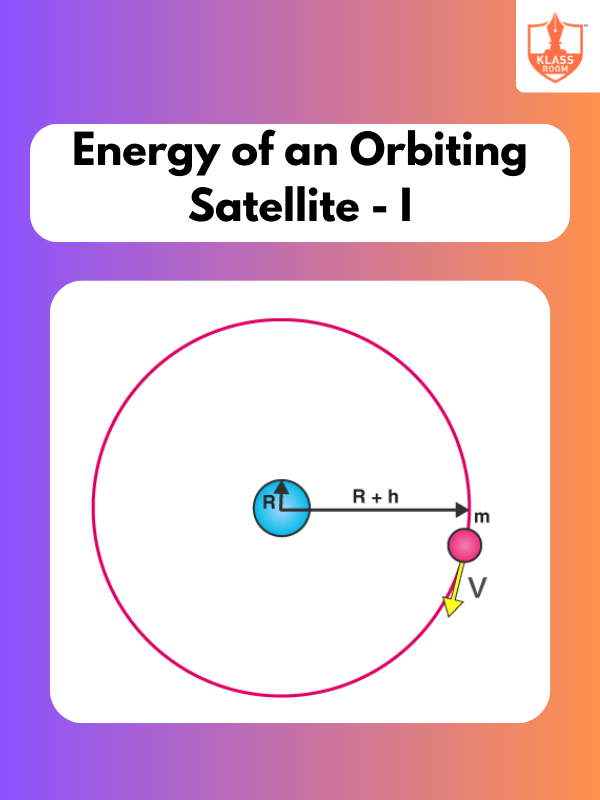
Energy of an Orbiting Satellite - I
Description: Energy of an Orbiting Satellite - I explains the kinetic and potential energy of satellites in stable orbits.
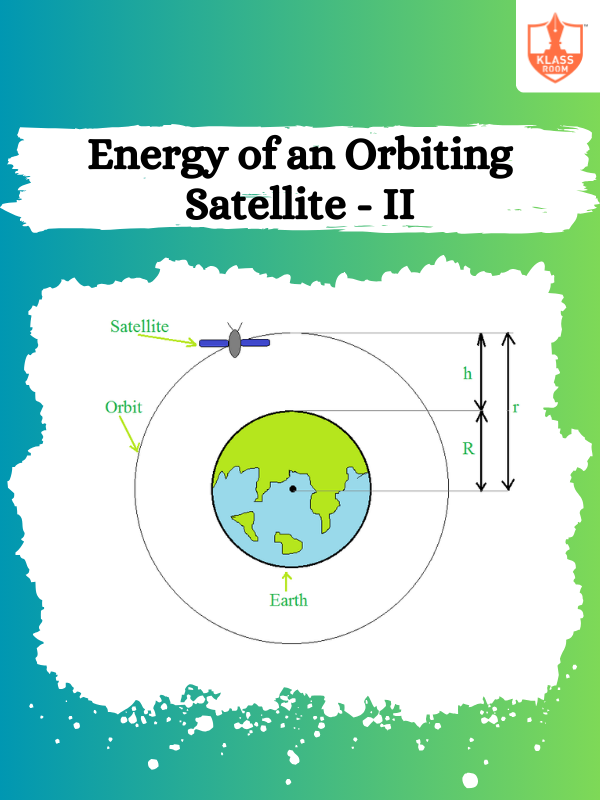
Energy of an Orbiting Satellite - II
Description: Energy of an Orbiting Satellite - II discusses the conservation of mechanical energy for orbiting satellites.
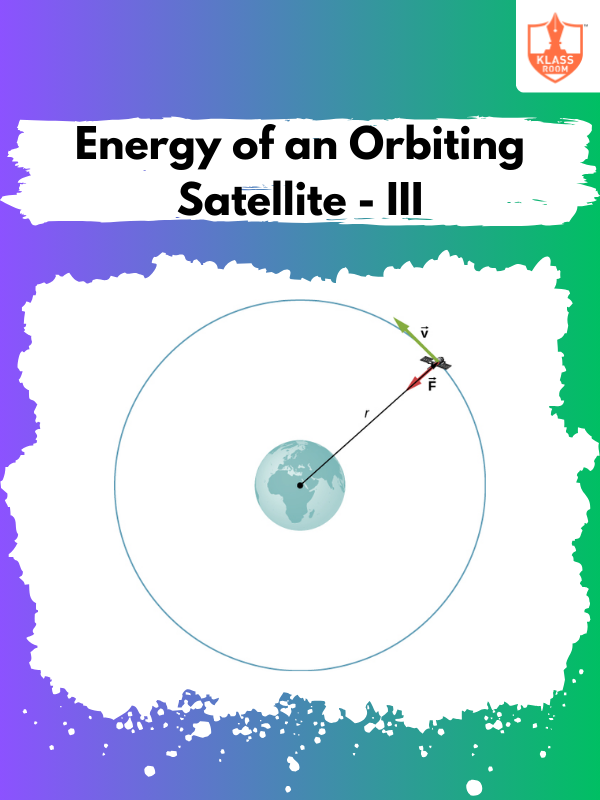
Energy of an Orbiting Satellite - III
Description: Energy of an Orbiting Satellite - III explores energy transfers during satellite orbit changes or deorbiting.

Geostationary and Polar Satellites - I
Description: Geostationary and Polar Satellites - I introduces the difference between geostationary and polar orbits and their applications.
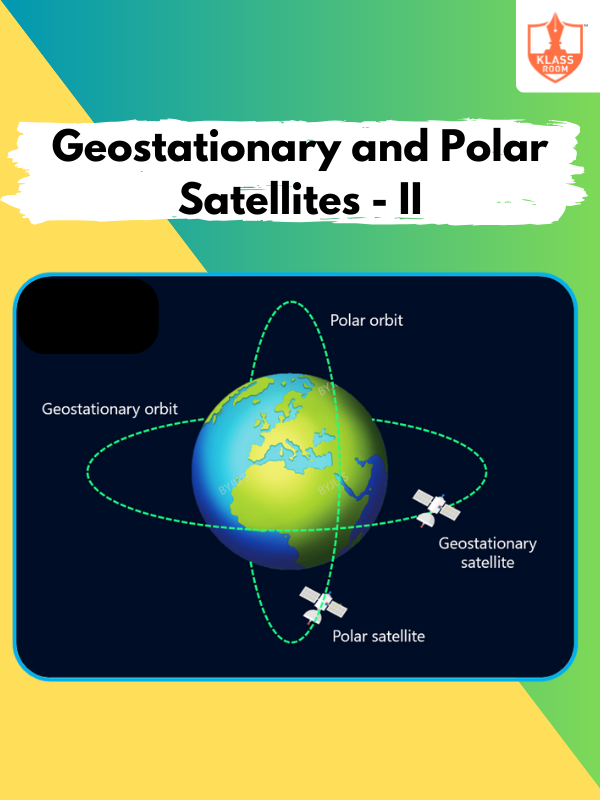
Geostationary and Polar Satellites - II
Description: Geostationary and Polar Satellites - II discusses the advantages of each orbit type in communication and Earth observation.

Weightlessness & Miscellaneous Questions - I
Description: Weightlessness & Miscellaneous Questions - I explains the concept of weightlessness experienced by astronauts in orbit.

Gravitational Potential - I
Description: "Gravitational Potential - I" explains the concept of gravitational potential energy and its calculation in gravitational fields.

Gravitational Potential - II
Description: "Gravitational Potential - II" explores gravitational potential due to spherical mass distributions and its impact on nearby objects.

.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)
.png)


.png)
.png)