Contents

Synopsis of Thermodynamics - I
Description: This section introduces thermodynamics, covering energy transfer, heat, work, and fundamental principles governing systems.
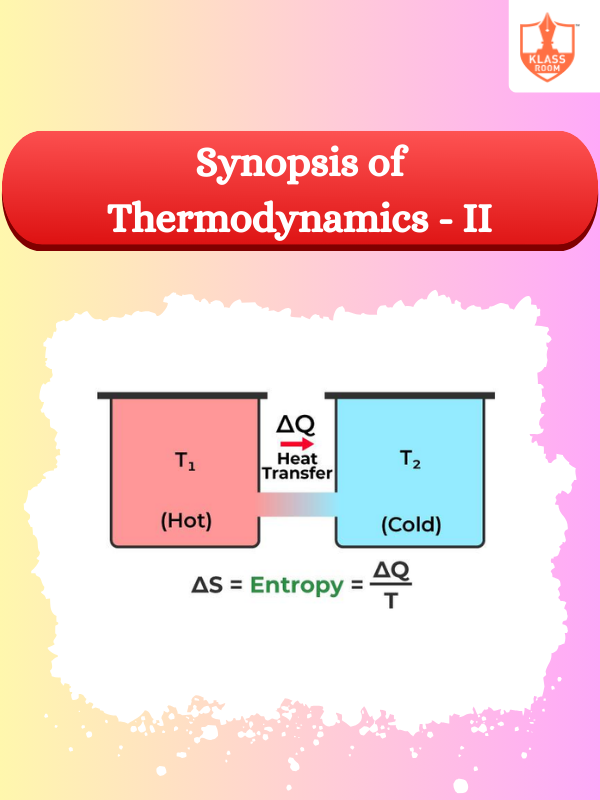
Synopsis of Thermodynamics - II
Description: This section explores advanced thermodynamic concepts, including laws of thermodynamics and their practical applications in systems.
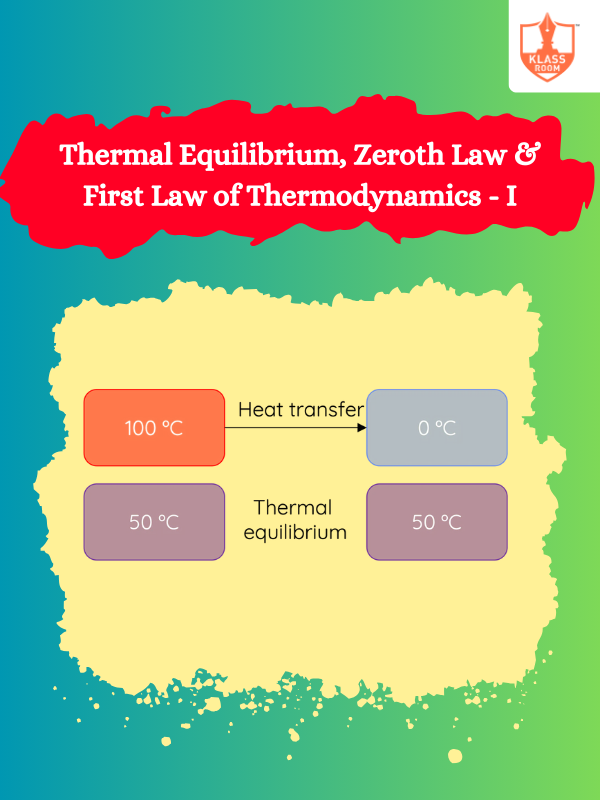
Thermal Equilibrium, Zeroth Law & First Law of Thermodynamics - I
Description: This section defines thermal equilibrium, introduces the zeroth law, and explains the first law of thermodynamics.
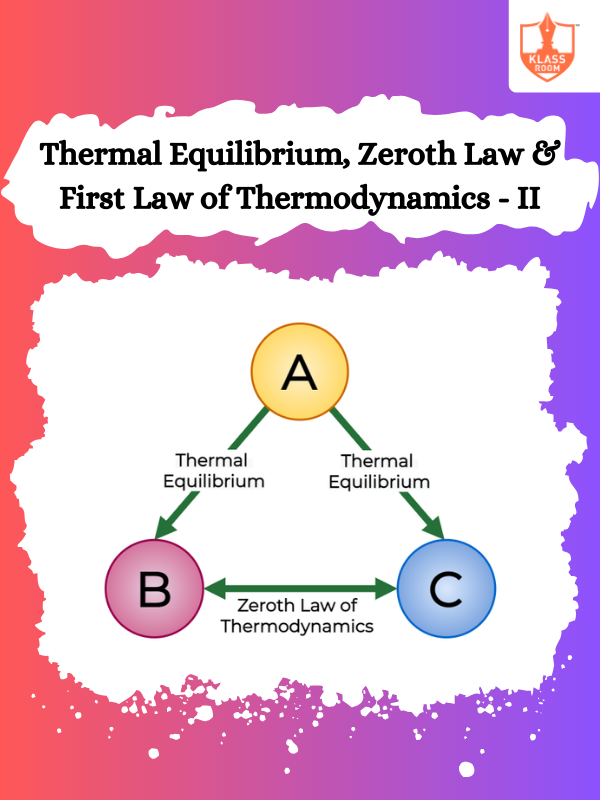
Thermal Equilibrium, Zeroth Law & First Law of Thermodynamics - II
Description: This section elaborates on the first law of thermodynamics, emphasizing energy conservation and heat transfer processes.
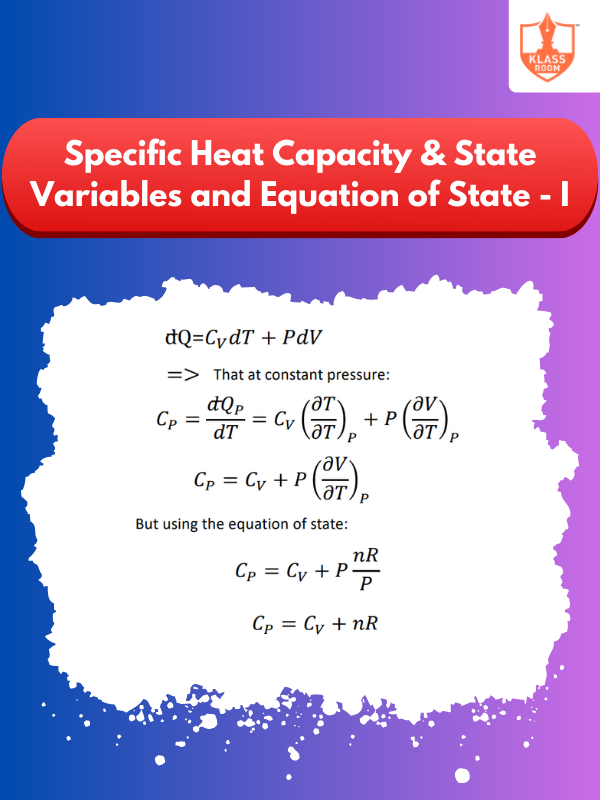
Specific Heat Capacity & State Variables and Equation of State - I
Description: This section defines specific heat capacity and introduces state variables for describing thermodynamic system conditions.
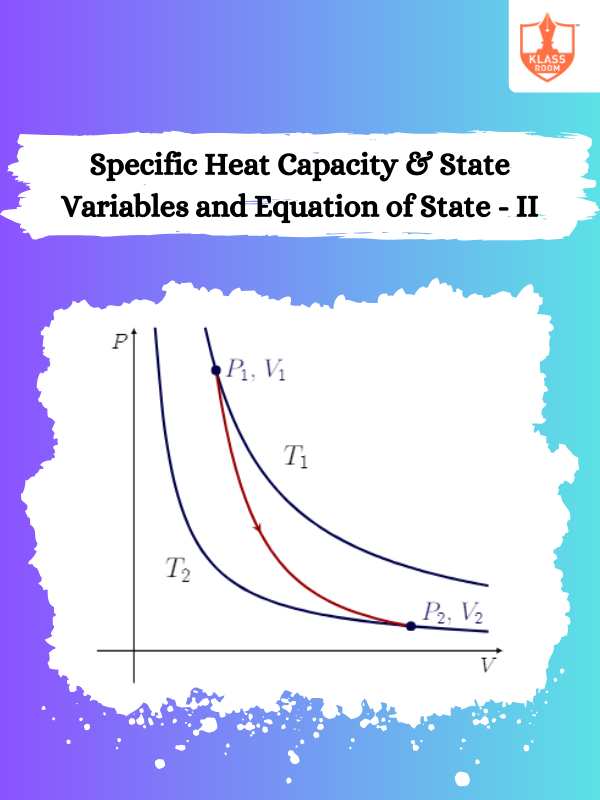
Specific Heat Capacity & State Variables and Equation of State - II
Description: This section explores relationships between state variables and specific heat capacity in thermodynamic processes and systems.
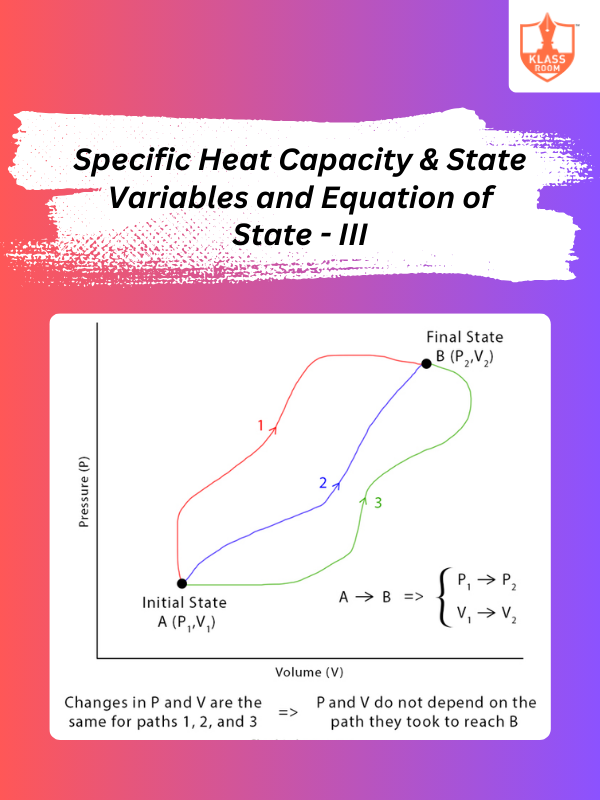
Specific Heat Capacity & State Variables and Equation of State - III
Description: This section analyzes equations of state, demonstrating how they describe gas behavior and thermodynamic properties.
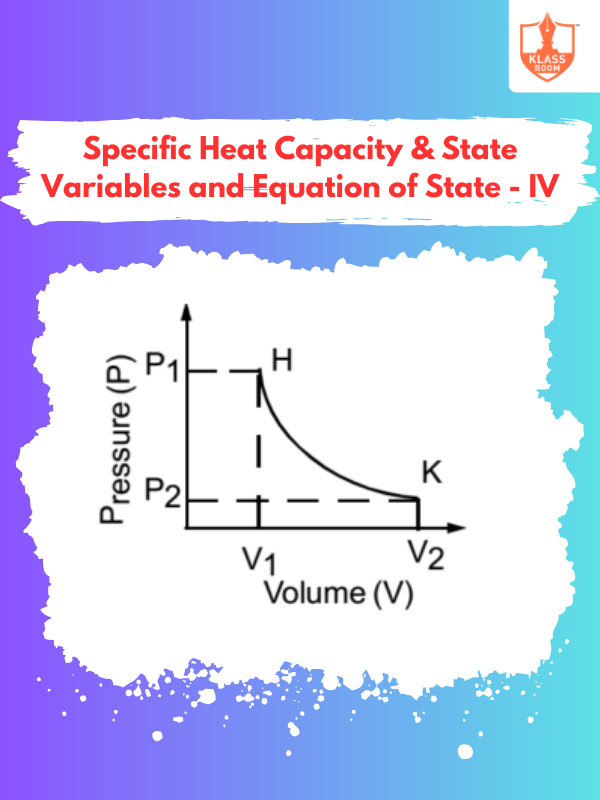
Specific Heat Capacity & State Variables and Equation of State - IV
Description: This section emphasizes practical applications of specific heat capacity and state variables in various thermodynamic scenarios.
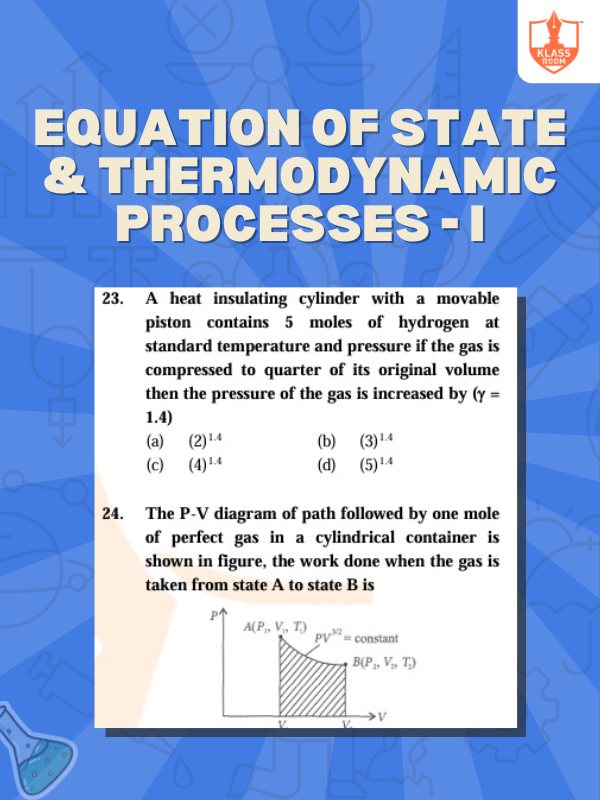
Equation of State & Thermodynamic Processes - I
Description: Equation of state relates variables like pressure, volume, and temperature; thermodynamic processes involve energy changes.
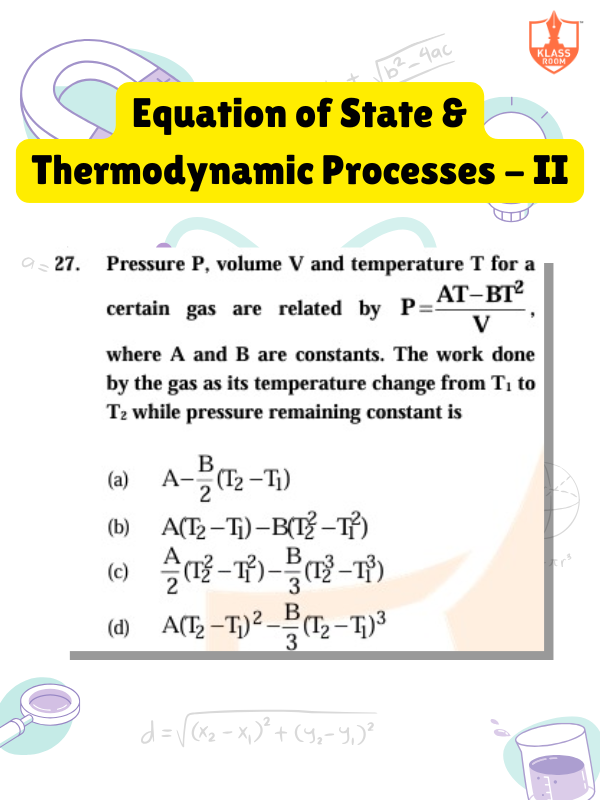
Equation of State & Thermodynamic Processes - II
Description: Equation of state relates pressure, volume, temperature; thermodynamic processes describe energy changes in systems.
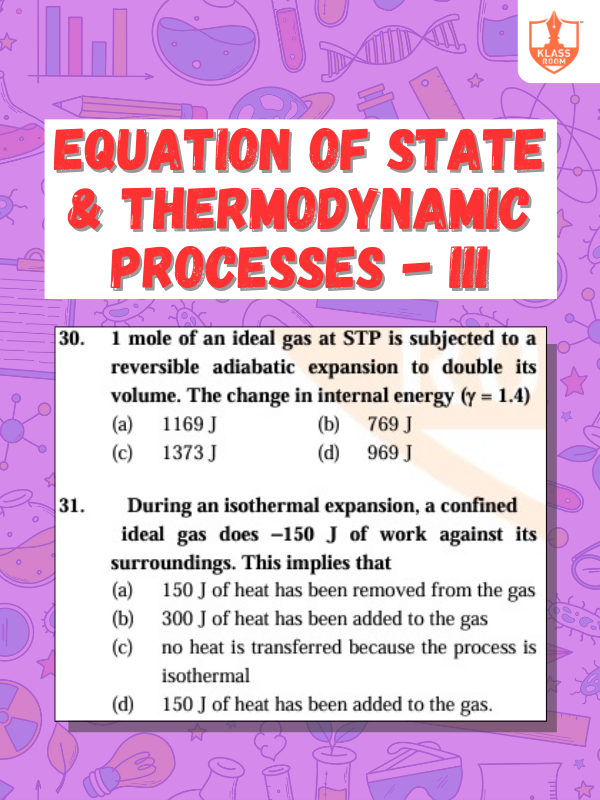
Equation of State & Thermodynamic Processes - III
Description: Equation of state links thermodynamic variables; processes include changes in energy, heat, and work interactions.
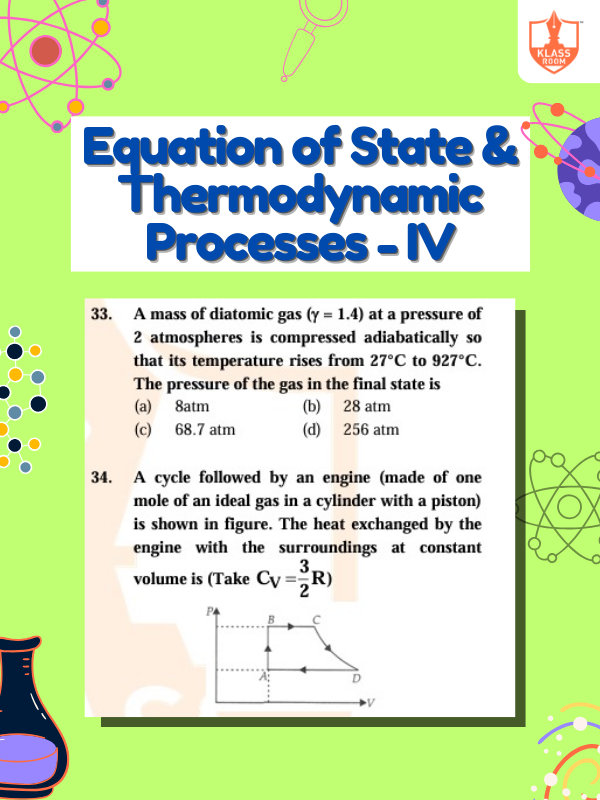
Equation of State & Thermodynamic Processes - IV
Description: Equation of state models system behavior; thermodynamic processes describe energy transformation under different conditions.
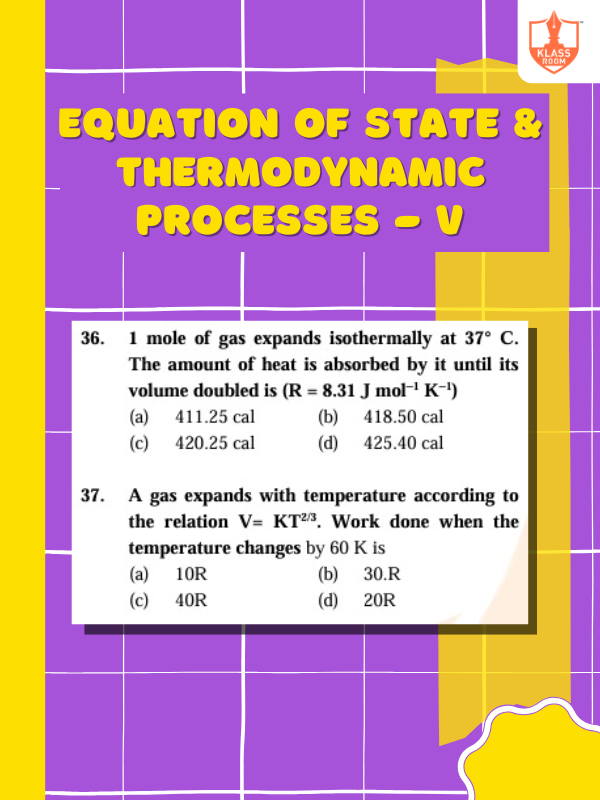
Equation of State & Thermodynamic Processes - V
Description: Equation of state expresses relationships between variables; thermodynamic processes describe energy changes, work, and heat.
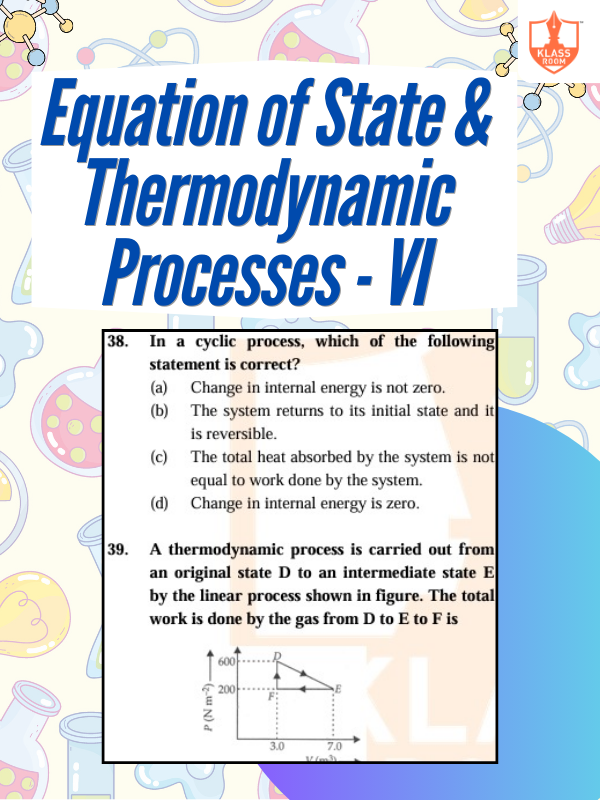
Equation of State & Thermodynamic Processes - VI
Description: Equation of state defines system state; thermodynamic processes involve energy, temperature, pressure, and volume changes.
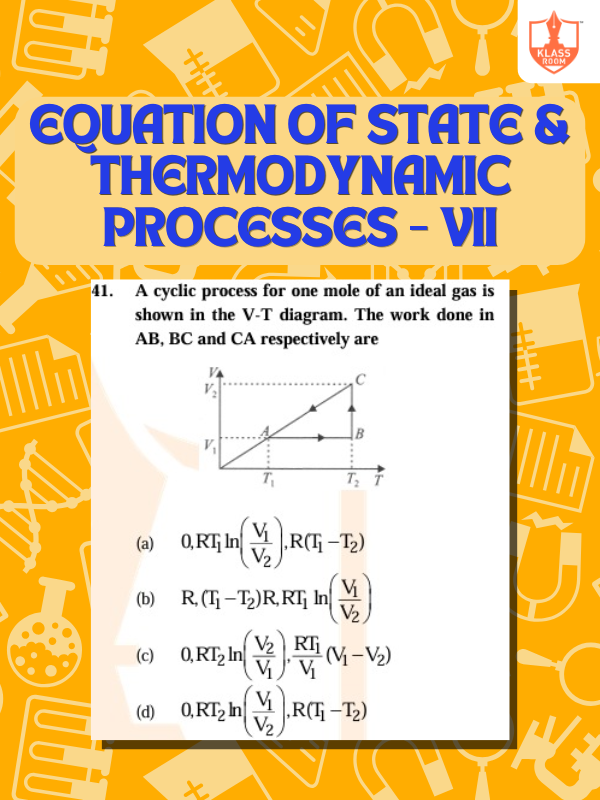
Equation of State & Thermodynamic Processes - VII
Description: Equation of state describes system behavior; thermodynamic processes involve work, heat, and energy transformations.
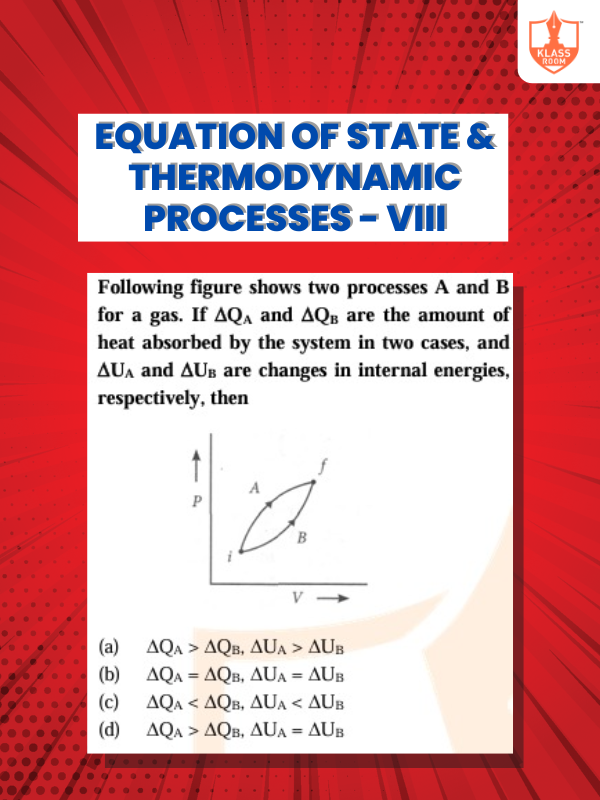
Equation of State & Thermodynamic Processes - VIII
Description: Equation of state defines system relations; thermodynamic processes involve energy transfer, work, and heat exchange.
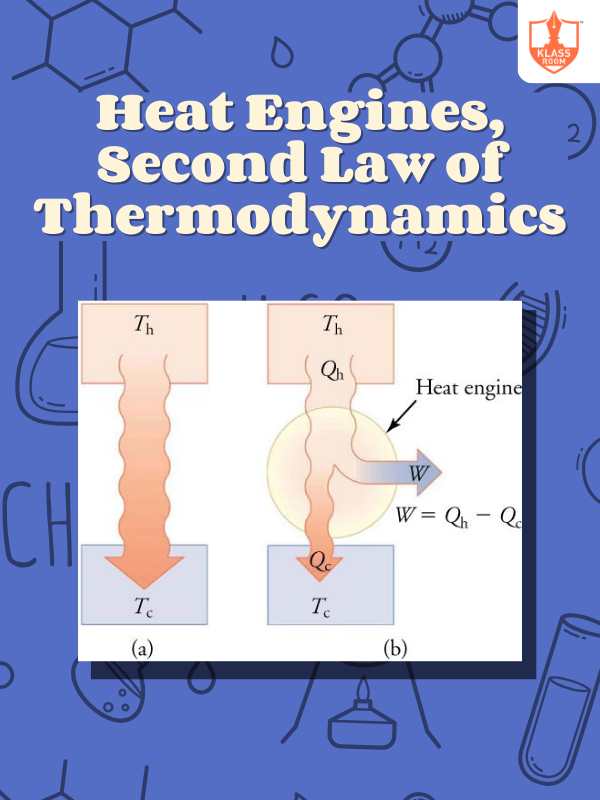
Heat Engines, Second Law of Thermodynamics
Description: Heat engines convert heat to work cyclically; second law forbids 100% efficiency, ensuring entropy increase.
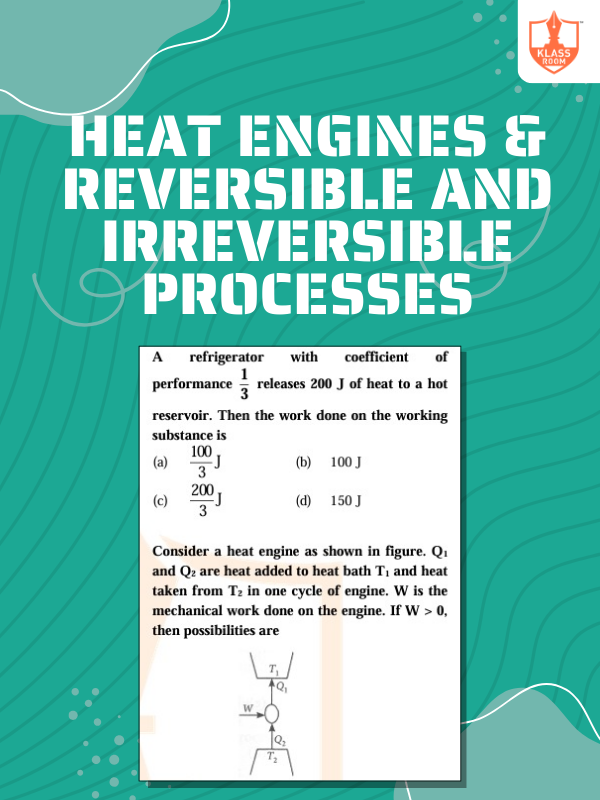
Heat Engines & Reversible and Irreversible Processes
Description: Heat engines convert heat to work; reversible processes are ideal, irreversible processes involve entropy increase.

Refrigerators & Second Law of Thermodynamics
Description: Refrigerators, heat pumps transfer heat; second law ensures energy input, prohibits spontaneous cold-to-hot flow.

Refrigerators & Reversible and Irreversible Processes
Description: Refrigerators transfer heat; reversible processes are ideal, irreversible processes increase entropy, reducing efficiency.

Refrigerators and Heat Pumps & Carnot Engine
Description: Refrigerators, heat pumps transfer heat; Carnot engine sets maximum efficiency limits based on temperature difference.
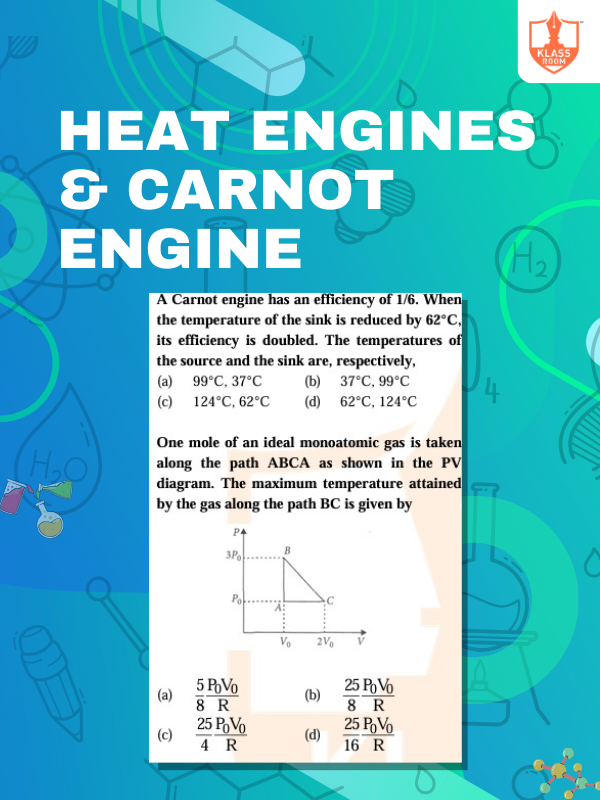
Heat Engines & Carnot Engine
Description: Heat engines convert heat to work; Carnot engine achieves maximum efficiency between two temperature reservoirs.

Specific Heat Capacity & Mean Free Path - II
Description: Heat required per unit mass to change temperature, and average molecular distance between successive collisions.

Specific Heat Capacity & Mean Free Path - III
Description: Explores variations in heat capacity, factors affecting mean free path, and real-life thermodynamic applications.
.png)

.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)
.png)


.png)
.png)