Contents

Course Outline
Description: A Course Outline details topics, objectives, schedule, and assessments, guiding students through the curriculum.
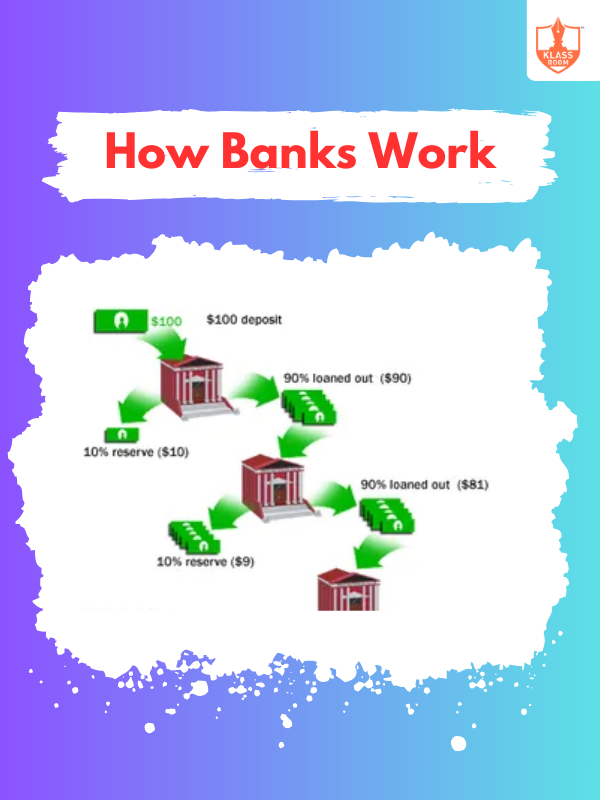
How Banks Work
Description: Banks accept deposits, provide loans, facilitate transactions, manage finances, and support economic growth.

Basics of Payment System
Description: Payment systems enable secure, efficient transfer of funds between parties through various electronic or physical methods.
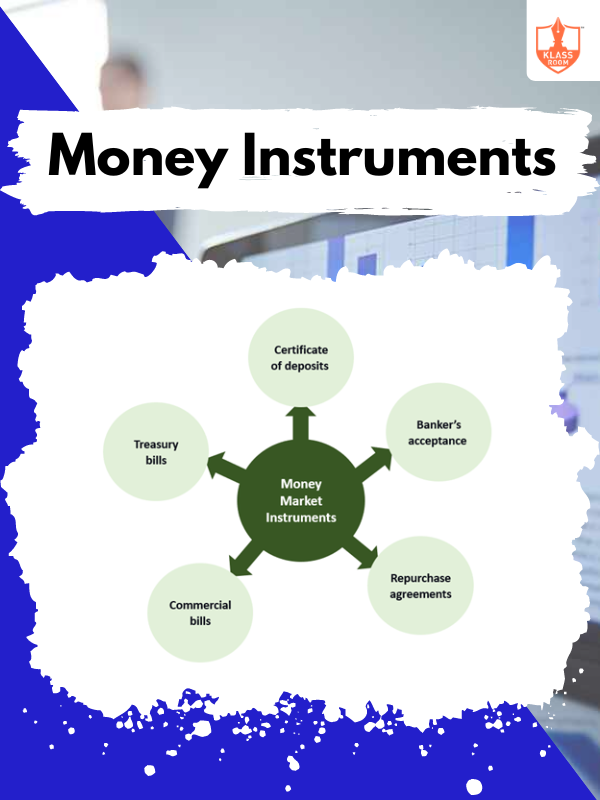
Money Instruments
Description: Money instruments include cash, checks, credit/debit cards, and digital wallets for making payments and transactions.
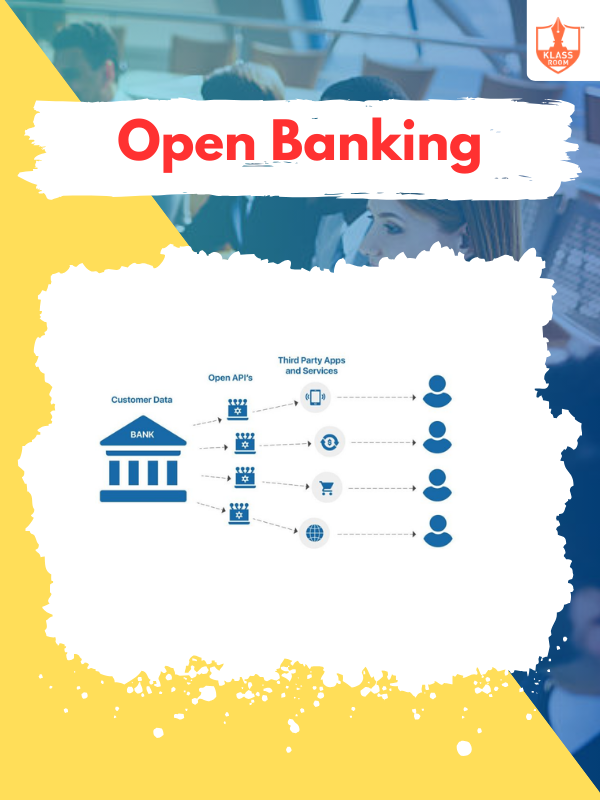
Open Banking
Description: Open Banking allows secure data sharing between banks and third parties, enhancing financial services and innovation.

UPI
Description: UPI (Unified Payments Interface) enables instant, real-time bank transfers using mobile devices, simplifying digital payments.

Card Payments
Description: Card payments use credit or debit cards to make transactions electronically, offering convenience and security.

BAAS
Description: BAAS (Banking-as-a-Service) provides banking functions via APIs, enabling fintech's to offer financial services seamlessly.

Regulation in India, UK, and US
Description: Regulation varies: India focuses on central authority, UK on independent bodies, and US on sector-specific agencies.
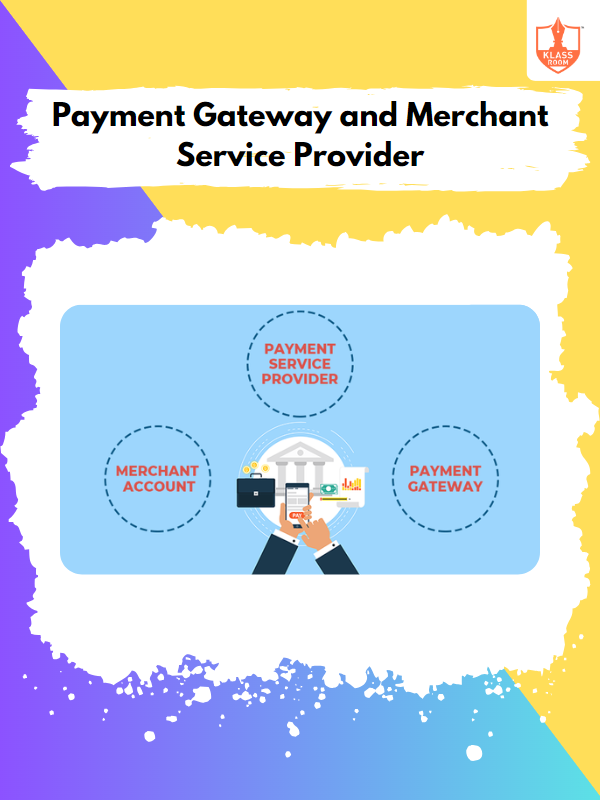
Payment Gateway and Merchant Service Provider
Description: Payment gateways process online transactions securely, while merchant service providers handle payment processing and merchant accounts.

KYB and AML
Description: KYB (Know Your Business) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) are processes to verify business legitimacy and prevent financial crimes.

Fraud Prevention
Description: Fraud prevention involves strategies and tools to detect, prevent, and mitigate fraudulent activities in businesses.
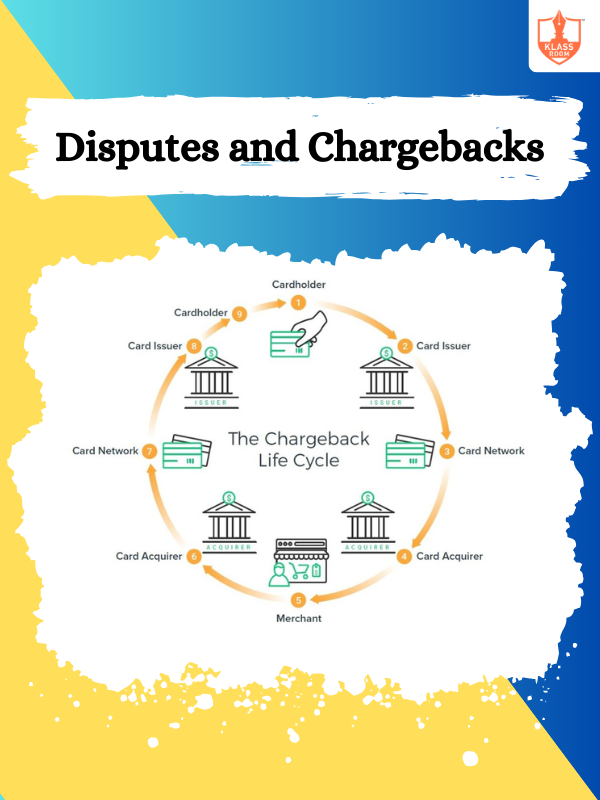
Disputes and Chargebacks
Description: Disputes and chargebacks involve customers contesting transactions, leading to potential refunds and merchant losses.

Types of Cards
Description: Types of cards include credit cards, debit cards, prepaid cards, charge cards, and gift cards.
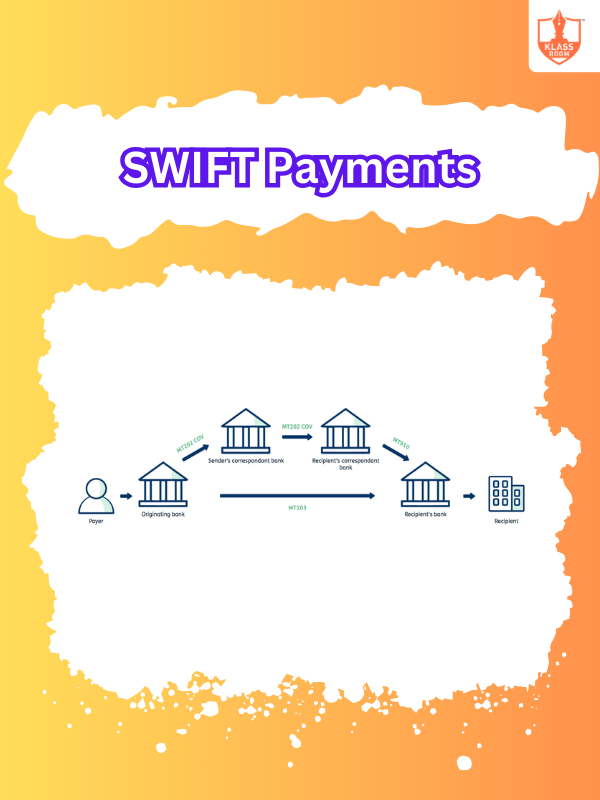
SWIFT Payments
Description: SWIFT payments are international money transfers conducted through the SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication) network, connecting banks globally.

Direct Debit
Description: Direct Debit is an automatic payment method where funds are withdrawn directly from a payer's bank account to pay recurring bills or subscriptions.

ACH Payment
Description: ACH (Automated Clearing House) payment is an electronic funds transfer system in the U.S. for processing direct deposits, bill payments, and other transactions between banks.

Intro to Fintech Apps
Description: Fintech apps streamline financial services like banking, payments, and investments, offering convenience and innovation
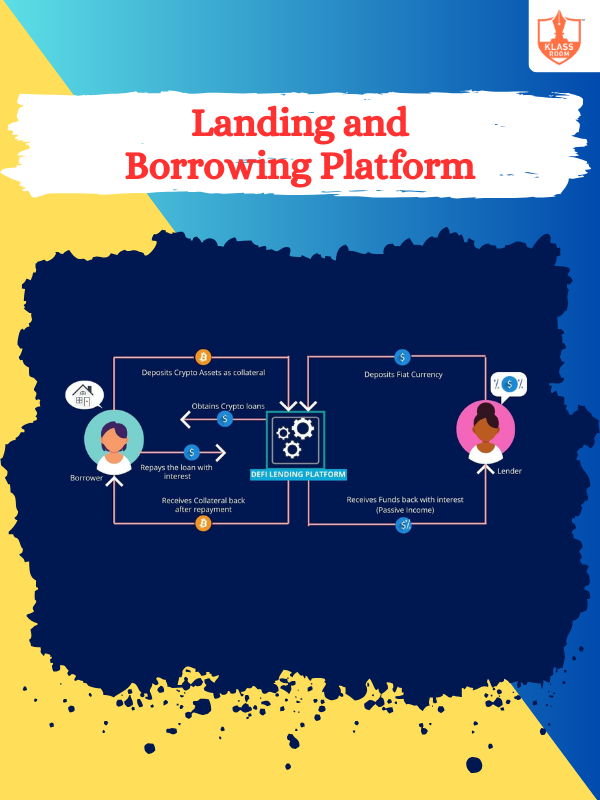
Landing and Borrowing Platform
Description: Lending and borrowing platforms connect borrowers with lenders online, facilitating peer-to-peer loans and alternative financing.

Payment Gateway and Embedded Finance
Description: Payment gateways enable secure online transactions, while embedded finance integrates financial services into non-financial platforms.
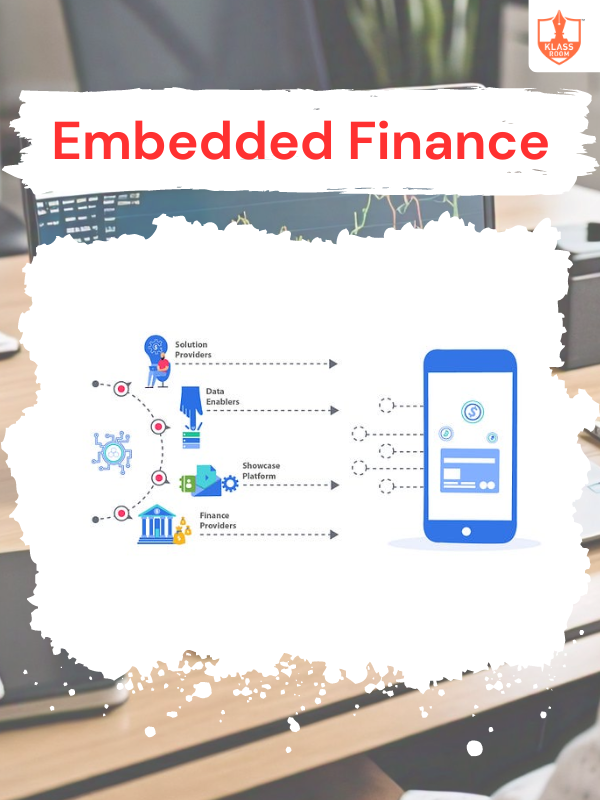
Embedded Finance
Description: Embedded finance integrates financial services like payments, lending, or insurance directly into non-financial platforms or apps.

Insurtech
Description: Insurtech leverages technology to innovate and improve insurance services, from underwriting to claims processing.

Investment Platform
Description: An investment platform provides tools and services for individuals to manage, invest, and grow their financial assets.
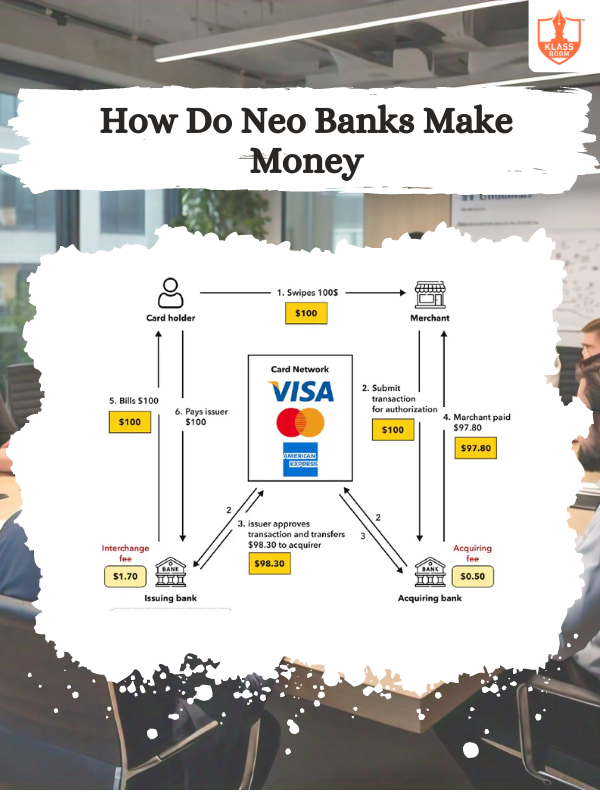
How Do Neo Banks Make Money
Description: Neobanks earn through interchange fees, subscription charges, interest margins, financial products, and partnerships.

Advanced Payment Technology - Part II
Description: Advanced payment technology enables secure, fast, and contactless transactions through digital platforms and innovative solutions.

DeFi
Description: DeFi, or decentralized finance, uses blockchain to create open, permissionless financial services without intermediaries.

E-Money and E-Wallet
Description: E-money represents digital currency, while e-wallets store and manage these funds for online transactions.

BaaS
Description: Banking as a Service (BaaS) offers financial services through APIs, enabling third-party integration with banks.

Web 1, 2, and 3
Description: Web 1: Static, read-only websites. Web 2: Interactive, user-generated content. Web 3: Decentralized, blockchain-based internet.





