Contents

Chemical Reaction & Very Fast Reaction
Description: Chemical reactions involve the transformation of reactants into products, with very fast reactions occurring instantly.

Rate, Speed & Velocity of Reaction
Description: Rate, speed, and velocity of reaction indicate how quickly reactants are converted into products over time.
Average Rate of Reactions
Description: Average rate of reaction measures concentration change of reactants or products over a specific time interval.
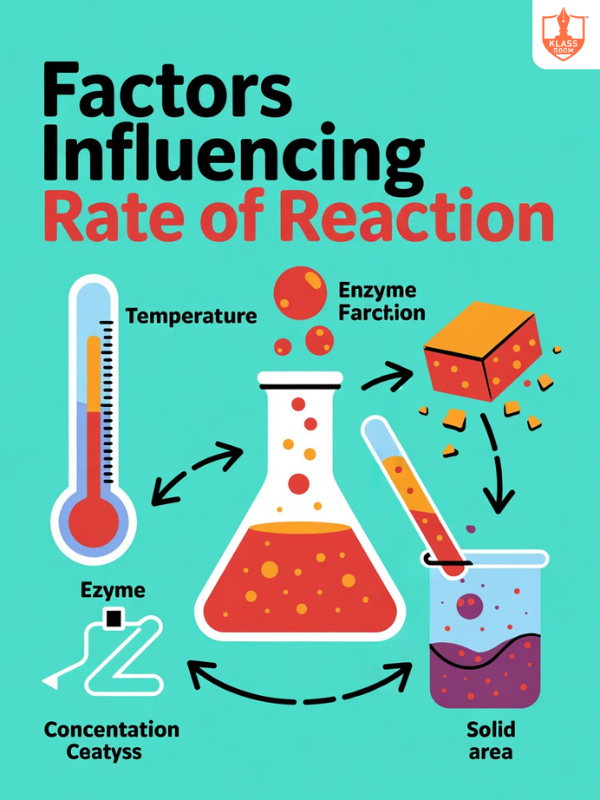
Factors influence the rate of reaction
Description: Factors influencing the rate of reaction include temperature, concentration, catalyst, surface area, and pressure.
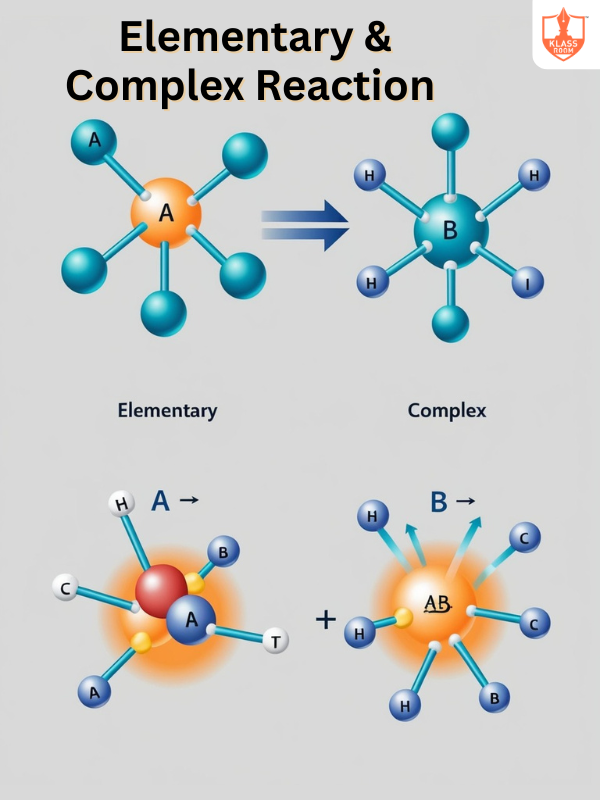
Elementary & Complex Reaction
Description: Elementary reactions occur in a single step, while complex reactions involve multiple steps and intermediates.

Order of reaction
Description: Order of reaction is the sum of exponents in the rate equation, determining reactant dependency.
Rate constant & its Characteristic
Description: Rate constant is a proportionality factor in rate equations, influenced by temperature and reaction order.
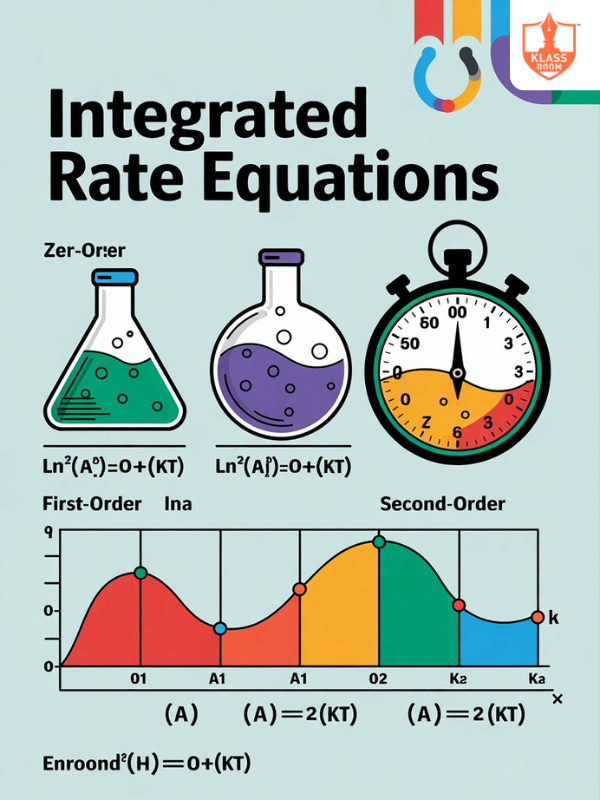
Integrated Rate Equations
Description: Integrated rate equations describe the change in reactant or product concentration over time mathematically.

Methods of Determination of Order of Reaction
Description: Methods to determine reaction order include graphical analysis, initial rate method, and half-life determination.
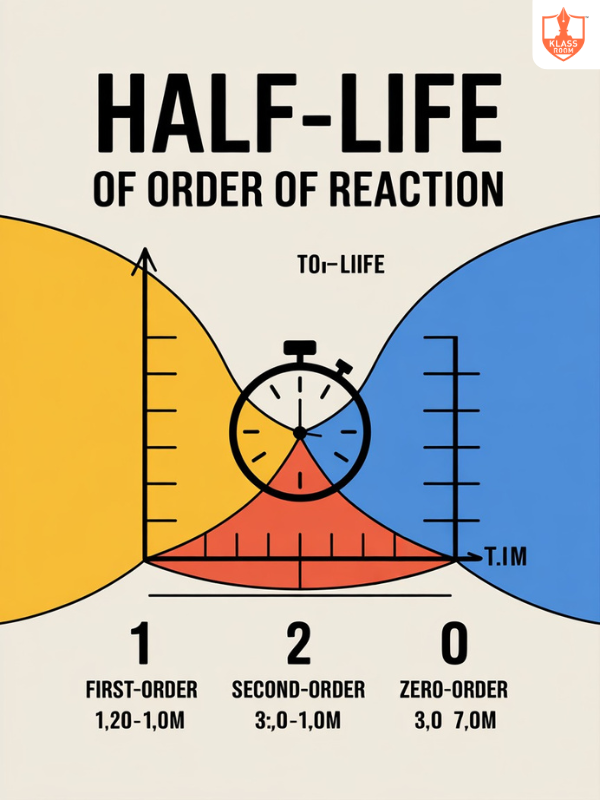
Half Life of order of Reaction
Description: Half-life of a reaction is the time required for half the reactant to be consumed.

Factors affecting rates of reactions
Description: Factors affecting reaction rates include the nature of reactants, temperature, concentration, catalysts, and physical state.
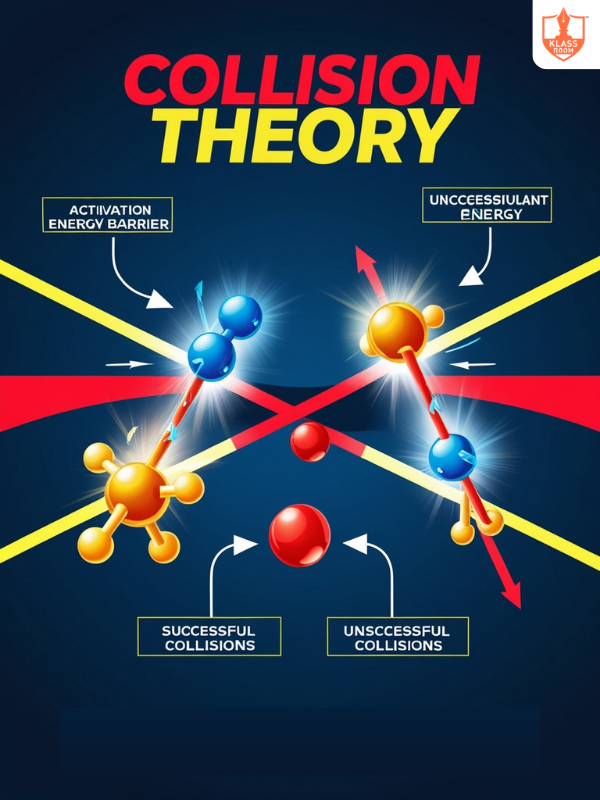
Collision Theory
Description: Collision theory states that reactant molecules must collide with proper orientation and energy to react.

Summary of the Chapter
Description: Summary of the chapter explains reaction rates, influencing factors, rate laws, reaction mechanisms, and theories.

Instantaneous rate of Reaction
Description: Instantaneous rate of reaction represents the reaction rate at a particular moment, determined using differential equations.



.png)