Contents

Introduction and Electronic Configuration of Gr. Ele. 13
Description: Group 13 elements have three valence electrons, forming diverse compounds with unique bonding properties.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Gr. Ele.13
Description: They exhibit varying reactivity, oxidation states, and different metallic or non-metallic characteristics.
Reactivity of Group Elements 13
Description: These elements react with oxygen, halogens, and other elements, forming compounds like oxides and halides.

Anomalous Properties of Boron
Description: Boron differs from other Group 13 elements due to its small size and unique bonding behavior.
Boron hydrides & Diborane
Description: Boron hydrides are compounds with boron and hydrogen, with diborane being a key example.
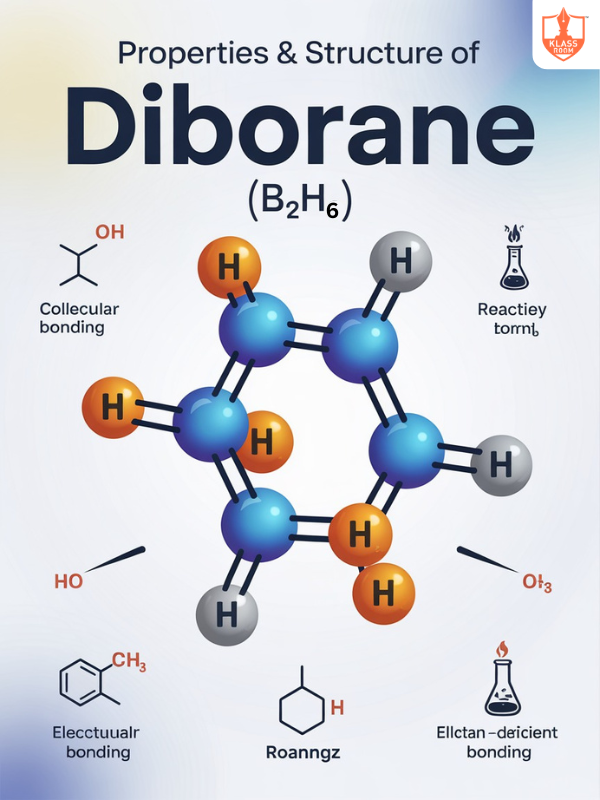
Properties & Structure of Diborane
Description: Diborane (B₂H₆) is a colorless, highly reactive gas with unusual bonding between boron atoms.

Introduction and Properties of Gr. Ele.14
Description: Group 14 elements have four valence electrons, forming diverse compounds, both metallic and non-metallic.
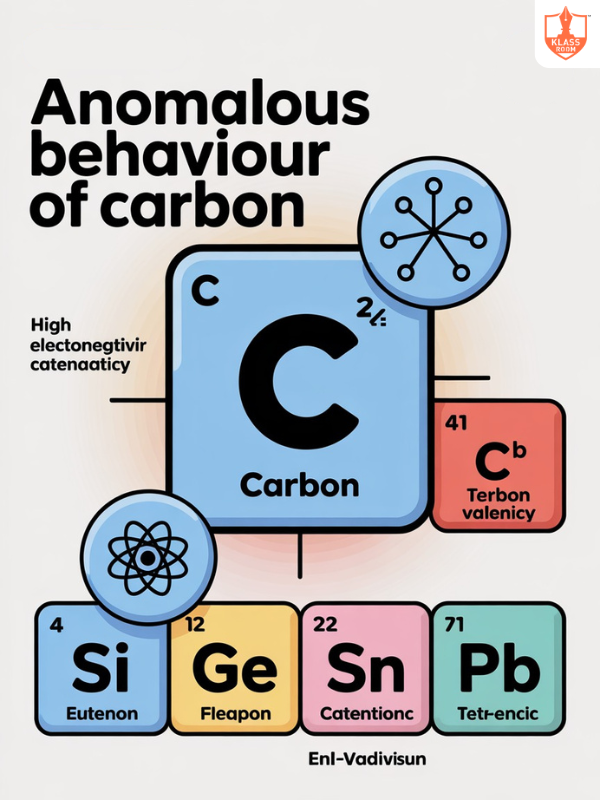
Anomalous behaviour of Carbon
Description: Carbon exhibits unique properties, including the ability to form multiple stable allotropes like diamond and graphite.

Fullerenes
Description: Fullerenes are carbon molecules forming spherical, tubular structures, with distinct electronic and physical properties.

Chemical Properties of Carbon
Description: Carbon reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, and can also form carbides with metals.
Silicon
Description: Silicon is a metalloid, widely used in semiconductors, with properties similar to carbon and germanium.

Group 15 Elements
Description: Group 15 elements include nitrogen and phosphorus, showing variable oxidation states and forming covalent compounds.
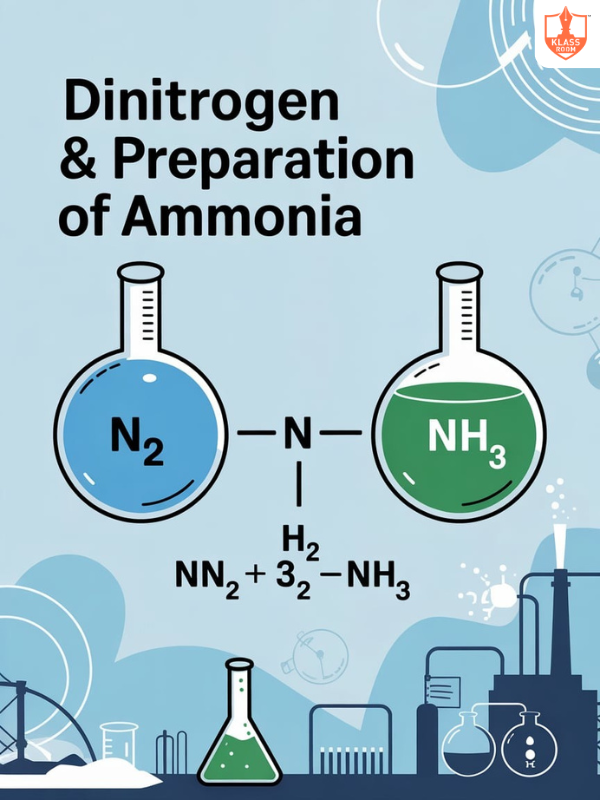
Dinitrogen and Preparation of Ammonia
Description: Dinitrogen is inert and abundant; ammonia is prepared industrially by Haber process using nitrogen and hydrogen.

Structure and Uses of Ammonia
Description: Ammonia has a trigonal pyramidal structure; used in fertilizers, cleaning agents, and nitric acid production.
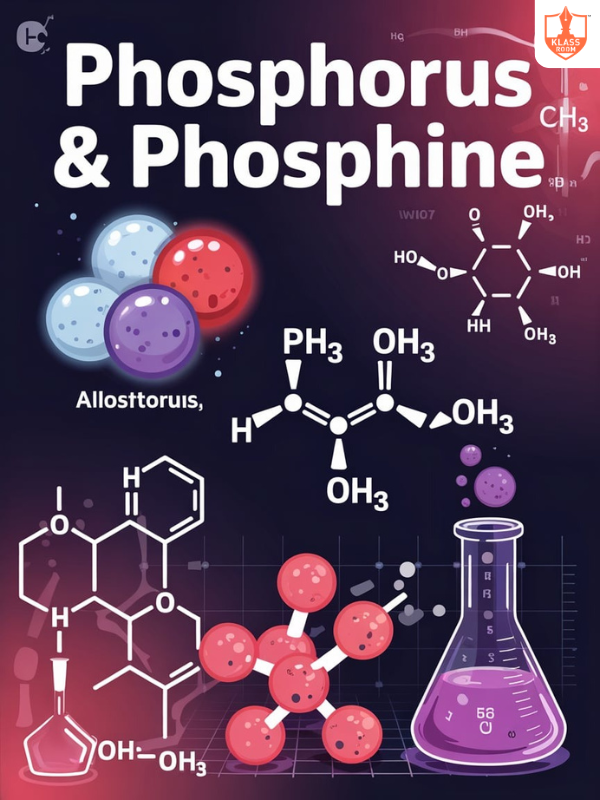
Phosphorus and Phosphine
Description: Phosphorus exists in several forms; phosphine is a toxic gas used in fumigation and semiconductors.

Phosphorus Pentachloride
Description: Phosphorus pentachloride is a yellow solid; used in chlorination reactions and preparation of organic chlorides.


.png)