Contents
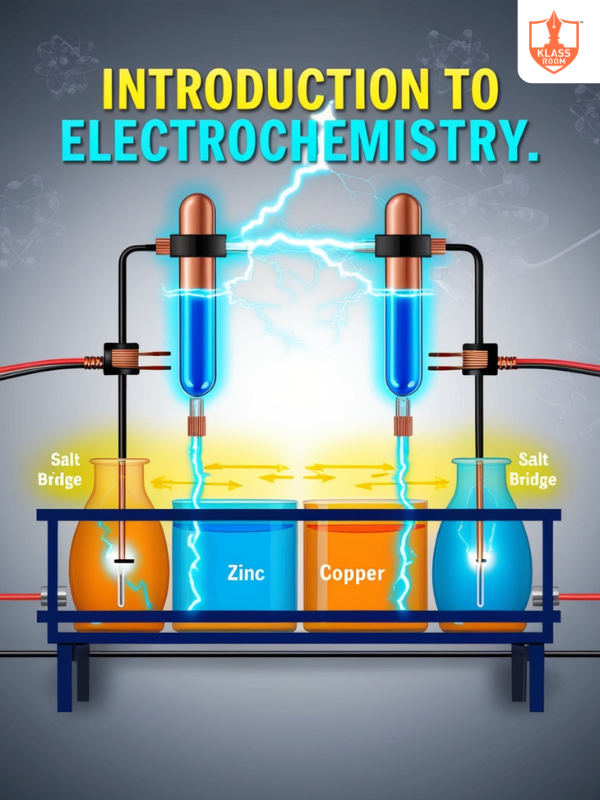
Introduction of Electrochemistry
Description: Study of chemical reactions involving electron transfer and electrical energy conversion.
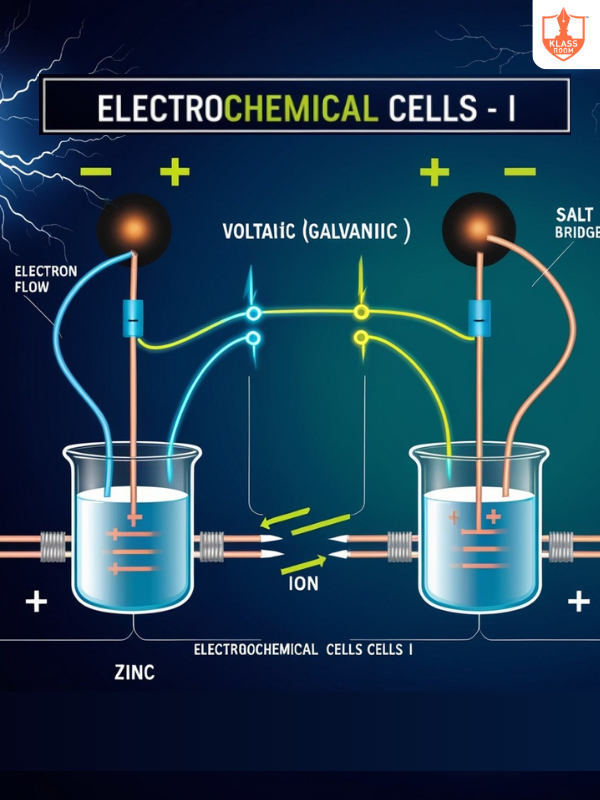
Electrochemical Cells - I
Description: Devices converting chemical energy into electrical energy through redox reactions.

Electrochemical Cells - II
Description: Comprises galvanic and electrolytic cells with distinct operational mechanisms.

IUPAC Convention
Description: Standardized nomenclature and representation of electrochemical reactions and cell notations.
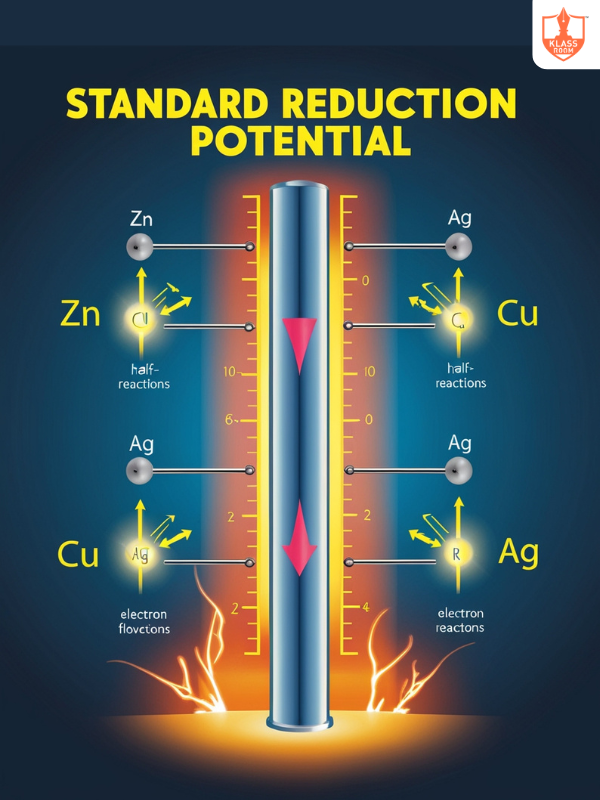
Standard Reduction Potential
Description: Potential of a half-cell under standard conditions relative to the hydrogen electrode.

Nernst Equation
Description: Calculates electrode potential considering ion concentration and temperature.

Nernst Equation for Cell
Description: Determines overall cell potential using standard potential and reaction quotient.

Electro Chemical Cell & Gibb's Energy
Description: Relates cell potential to Gibbs free energy, indicating spontaneity of reaction.

Conductance of Electrolytic Solution
Description: Measures the ability of ions in solution to conduct electricity.
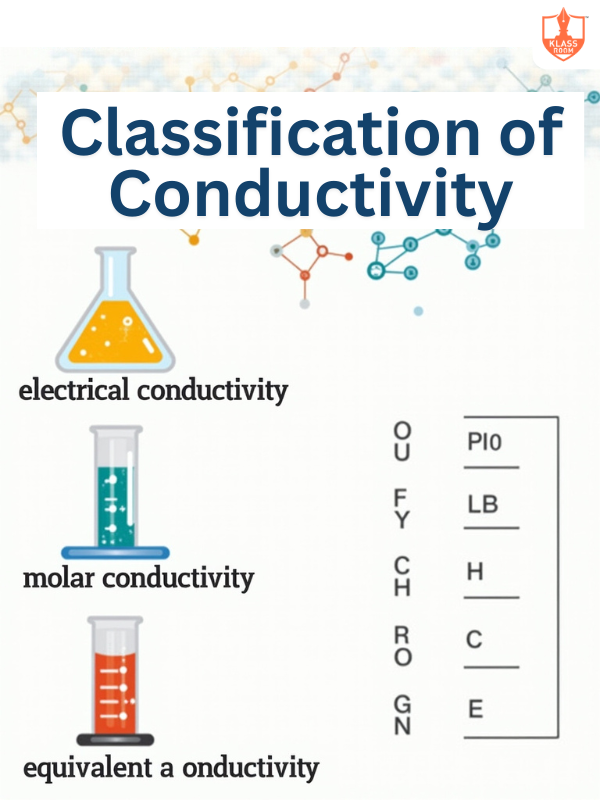
Classification of conductivity
Description: Includes specific, molar, and equivalent conductivity based on ion concentration.

Measurement of the conductivity of the ionic cell
Description: Involves Wheatstone bridge and conductivity cell for precise measurement.

Effect of Concentration or Dilution
Description: Conductivity decreases with dilution due to reduced ion interaction.
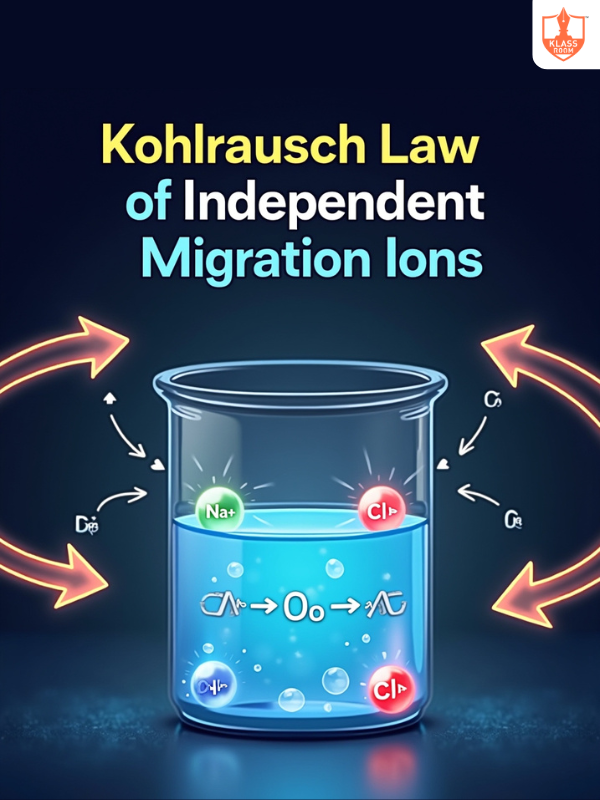
Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions
Description: States that individual ion conductivities remain constant at infinite dilution.
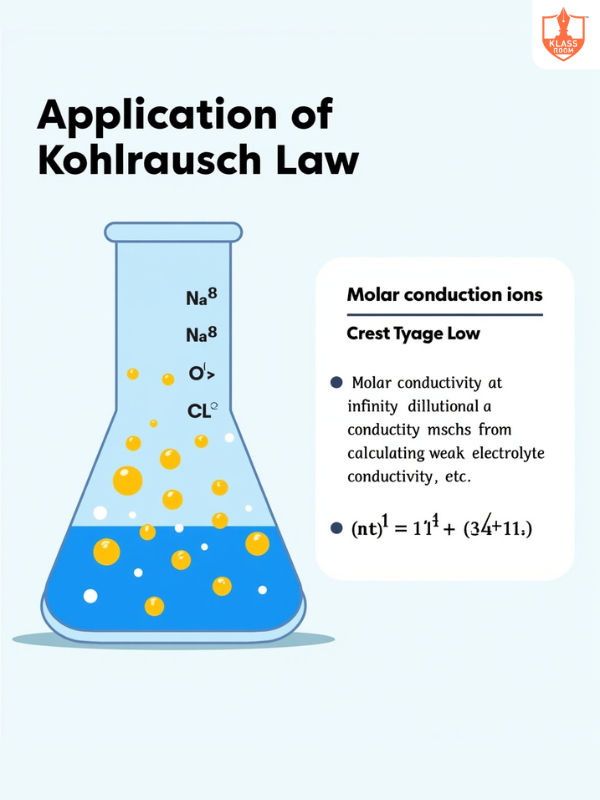
Application of Kohlrausch law
Description: Used to determine weak electrolyte dissociation and ion transport numbers.
Electrolytic cells and Electrolysis & Faraday's Laws
Description: Electrolysis involves redox reactions; Faraday’s laws relate charge, mass, and chemical changes.

Second Law of Faraday's Electrolysis
Description: Mass deposited is proportional to charge passed and equivalent weight of substance.

Second Law of Faraday's Electrolysis
Description: Mass deposited is proportional to charge passed and equivalent weight of substance.
Batteries - I
Description: Convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy for practical applications.

Batteries - II
Description: Classified as primary and secondary batteries based on rechargeability.
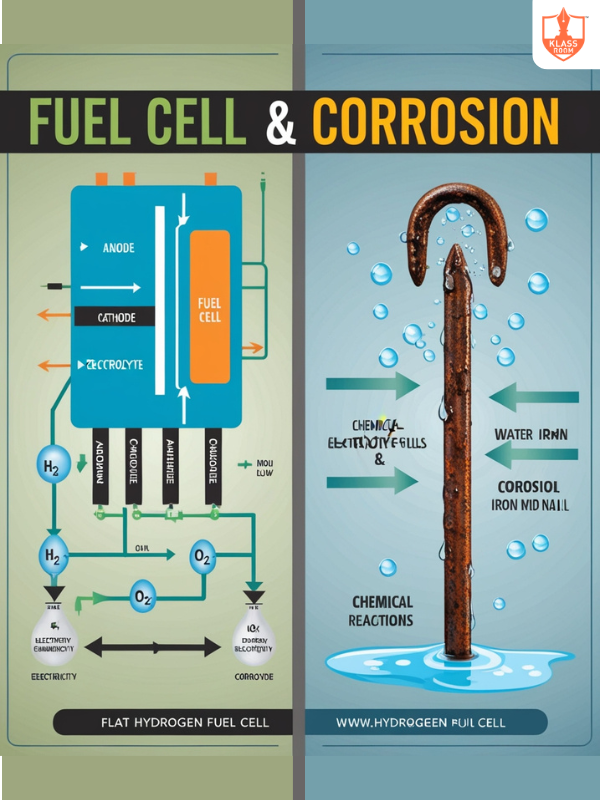
Fuel Cell & Corrosion
Description: Generate electricity from fuel oxidation; corrosion involves metal deterioration due to oxidation.



.png)