Contents
Organic Chemistry
Description: "Introduction to organic chemistry delves into the study of carbon compounds, their structures, properties, and reactions, forming the foundation of various fields including medicine, materials, and industry."
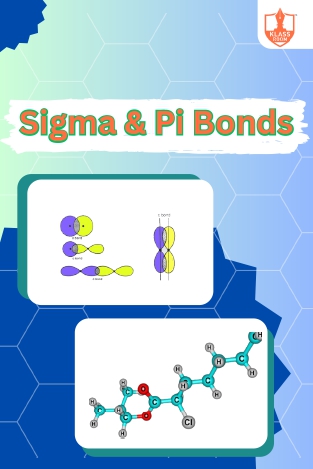
Sigma and Pi bonds
Description: Sigma and pi bonds describe electron distribution in covalent bonds. Organic compounds exhibit diverse structures, properties, and reactivity due to carbon's ability to form stable bonds with various elements.

Homologous & IUPAC
Description: Homologous series comprises compounds with similar functional groups and structural features, differing by a common increment. IUPAC nomenclature provides systematic rules for naming organic compounds, ensuring clarity and consistency.
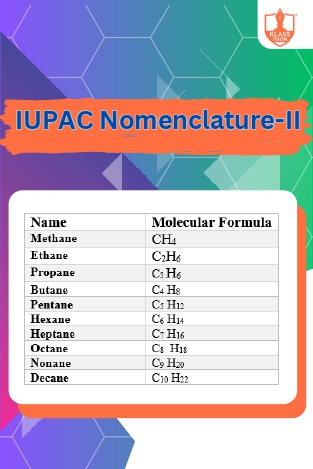
IUPAC Nomenclature-II
Description: IUPAC nomenclature-II expands on systematic naming rules for organic compounds, including complex structures and functional groups, ensuring precise and unambiguous identification in chemical communication and research.
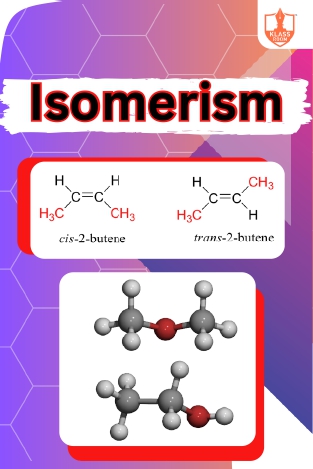
Isomerism
Description: Isomerism occurs when molecules share the same molecular formula but have different structural arrangements or spatial orientations. Classification includes structural, stereoisomerism, and functional isomerism based on differences in arrangement.

Reaction Mechanism
Description: Reaction mechanism elucidates step-by-step pathways by which reactants transform into products. Reagents initiate or participate in chemical reactions, while reaction intermediates form transiently during reaction progress, influencing overall kinetics an
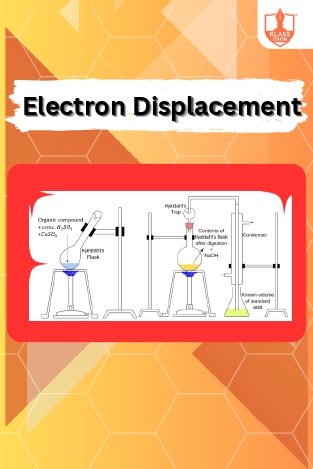
Electron Displacement
Description: Electron displacement effects describe how electron-rich or -deficient groups influence organic reactions. Types of organic reactions include substitution, addition, elimination, and rearrangement, each characterized by distinct mechanisms and outcomes.
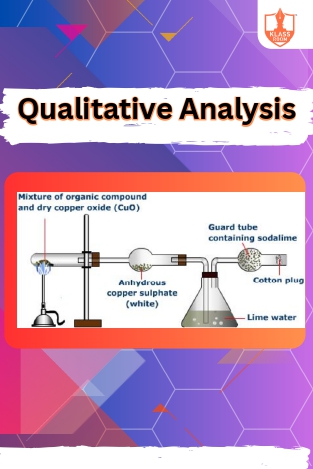
Qualitative Analysis
Description: Qualitative analysis of organic compounds involves identifying functional groups and structural features through various chemical tests and spectroscopic techniques, aiding in compound characterization and classification.

Quantitative Analysis
Description: Quantitative elemental analysis determines the composition of organic compounds by measuring the amounts of elements present. Techniques include combustion analysis, elemental analysis, and spectroscopic methods for accurate quantification.



.png)