Contents
.png)
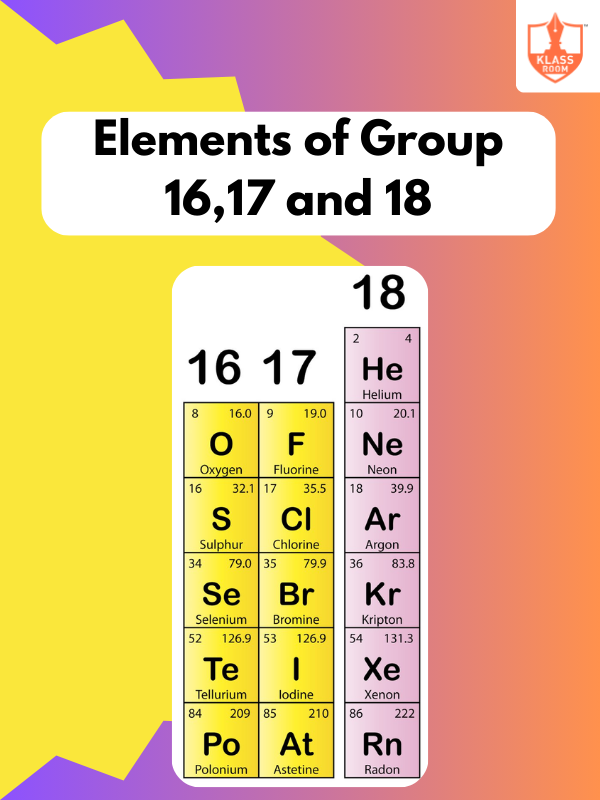
Modern Periodic Table
Description: Periodic Table organizes elements by increasing atomic number. Newlands’s Law of Octaves and Lothar Meyer’s contributions preceded Mendeleev’s Periodic Table. Modern Periodic Table refines this, including elements with atomic numbers > 100.
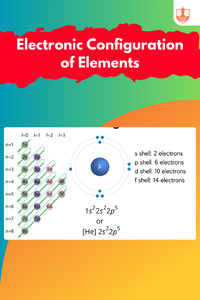
Electronic Configuration of Elements
Description: Electronic configuration details how electrons are distributed in shells and subshells. Periodic tables classify elements by properties and atomic number.

Ionic Radius & Lanthanide Contraction
Description: Metals, non-metals, and metalloids exhibit different physical and chemical properties. Ionic radius varies with atomic size, and lanthanide contraction affects atomic radii in the lanthanide series.
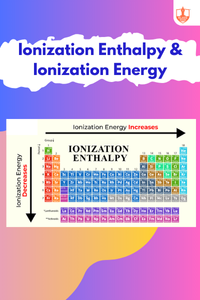
Ionization Enthalpy & Ionization Energy
Description: Ionization enthalpy refers to the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. It generally increases across periods and decreases down groups in the periodic table.

Electron Gain Enthalpy & Trends of Oxides
Description: Electron gain enthalpy measures energy released when gaining an electron; electronegativity gauges electron attraction in bonds.
.png)


.png)